Proteomics approach to study the functions of Drosophila myosin VI through identification of multiple cargo-binding proteins
- PMID: 21368190
- PMCID: PMC3078346
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1101415108
Proteomics approach to study the functions of Drosophila myosin VI through identification of multiple cargo-binding proteins
Abstract
Myosin VI is a molecular motor implicated in many processes, and it likely associates with a variety of cargoes that specify its functions. Although it is critical to Drosophila development, little is known about its cellular roles. To reveal its involvement in specific pathways, we sought to identify the binding partners of Drosophila myosin VI. We used affinity chromatography and mass spectrometry to discover interacting proteins, which we tested for direct binding. Using this approach, we found that the microtubule-associated protein Cornetto bound myosin VI, and we demonstrated a role for both in secretion of the lipidated morphogen Hedgehog. We also identified a number of other binding proteins, and further characterization of their interactions with myosin VI will advance our understanding of the roles of these complexes in cellular and developmental processes. Thus, our method has provided us the means to gain valuable insight into the multifaceted roles of a motor protein in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


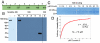
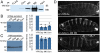
Comment in
-
Multifunctional myosin VI has a multitude of cargoes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Apr 12;108(15):5927-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1103086108. Epub 2011 Apr 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21464329 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- De La Cruz EM, Ostap EM. Relating biochemistry and function in the myosin superfamily. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004;16:61–67. - PubMed
-
- O’Connell CB, Tyska MJ, Mooseker MS. Myosin at work: Motor adaptations for a variety of cellular functions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1773:615–630. - PubMed
-
- Krendel M, Mooseker MS. Myosins: Tails (and heads) of functional diversity. Physiology. 2005;20:239–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

