Signaling by vitamin A and retinol-binding protein regulates gene expression to inhibit insulin responses
- PMID: 21368206
- PMCID: PMC3060239
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1011115108
Signaling by vitamin A and retinol-binding protein regulates gene expression to inhibit insulin responses
Abstract
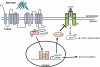
It currently is believed that vitamin A, retinol, functions through active metabolites: the visual chromophore 11-cis-retinal, and retinoic acids, which regulate gene transcription. Retinol circulates in blood bound to retinol-binding protein (RBP) and is transported into cells by a membrane protein termed "stimulated by retinoic acid 6" (STRA6). We show here that STRA6 not only is a vitamin A transporter but also is a cell-surface signaling receptor activated by the RBP-retinol complex. Association of RBP-retinol with STRA6 triggers tyrosine phosphorylation, resulting in recruitment and activation of JAK2 and the transcription factor STAT5. The RBP-retinol/STRA6/JAK2/STAT5 signaling cascade induces the expression of STAT target genes, including suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3), which inhibits insulin signaling, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ), which enhances lipid accumulation. These observations establish that the parental vitamin A molecule is a transcriptional regulator in its own right, reveal that the scope of biological functions of the vitamin is broader than previously suspected, and provide a rationale for understanding how RBP and retinol regulate energy homeostasis and insulin responses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Signaling by vitamin A and retinol-binding protein in regulation of insulin responses and lipid homeostasis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jan;1821(1):168-76. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.07.002. Epub 2011 Jul 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 21782034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The retinol esterifying enzyme LRAT supports cell signaling by retinol-binding protein and its receptor STRA6.FASEB J. 2014 Jan;28(1):26-34. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-234310. Epub 2013 Sep 13. FASEB J. 2014. PMID: 24036882 Free PMC article.
-
Transthyretin blocks retinol uptake and cell signaling by the holo-retinol-binding protein receptor STRA6.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Oct;32(19):3851-9. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00775-12. Epub 2012 Jul 23. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22826435 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin A in regulation of insulin responsiveness: mini review.Proc Nutr Soc. 2016 May;75(2):212-5. doi: 10.1017/S0029665115004322. Epub 2016 Jan 5. Proc Nutr Soc. 2016. PMID: 26729422 Review.
-
Cross talk between signaling and vitamin A transport by the retinol-binding protein receptor STRA6.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Aug;32(15):3164-75. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00505-12. Epub 2012 Jun 4. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22665496 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Intestinal Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Enrichment of Genes Associated with Immune and Lipid Mechanisms, Favoring Soybean Meal Tolerance in High-Growth Zebrafish (Danio Rerio).Genes (Basel). 2021 May 8;12(5):700. doi: 10.3390/genes12050700. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34066767 Free PMC article.
-
Increased unbound retinol-binding protein 4 concentration induces apoptosis through receptor-mediated signaling.J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 23;287(13):9694-9707. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.301721. Epub 2012 Feb 3. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22308028 Free PMC article.
-
RBP4 promotes denervation-induced muscle atrophy through STRA6-dependent pathway.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2024 Aug;15(4):1601-1615. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13518. Epub 2024 Jun 21. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2024. PMID: 39031684 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of Serum Retinol and Atherogenic Indices in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Case-Control Study.Indian J Clin Biochem. 2022 Jan;37(1):100-106. doi: 10.1007/s12291-020-00951-0. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35125699 Free PMC article.
-
All trans retinoic acid as a host-directed immunotherapy for tuberculosis.Curr Res Immunol. 2022 Mar 30;3:54-72. doi: 10.1016/j.crimmu.2022.03.003. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35496824 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McCollum EV, Davis M. The necessity of certain lipins in the diet during growth. J Biol Chem. 1913;15:167–175. - PubMed
-
- Osborne TB, Mendel LB. The vitamins in green foods. J Biol Chem. 1919;37:187–200.
-
- Noy N. In: Vitamin A Biochemical, Physiological, and Molecular Aspects of Human Nutrition. 2nd Ed. Stipanuk MH, editor. St. Louis: Saunders Elsevier; 2006.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

