A brief history of IL-9
- PMID: 21368237
- PMCID: PMC3074408
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003049
A brief history of IL-9
Abstract
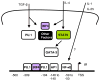
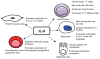
IL-9 was first described in the late 1980s as a member of a growing number of cytokines that had pleiotropic functions in the immune system. Although many biological functions have been attributed to IL-9, it remains an understudied cytokine. A resurgence of interest in IL-9 has been spurred by recent work demonstrating a role for IL-9 in regulating inflammatory immunity and defining the transcription factors that activate the Il9 gene in cells that most efficiently produce IL-9. In this review, we summarize the characterization of IL-9 biological activities, highlight roles for the cytokine that are clearly defined, and outline questions regarding IL-9 functions that still require further exploration.
Figures
References
-
- Hultner L, Druez C, Moeller J, Uyttenhove C, Schmitt E, Rude E, Dormer P, Van Snick J. Mast cell growth-enhancing activity (MEA) is structurally related and functionally identical to the novel mouse T cell growth factor P40/TCGFIII (interleukin 9) Eur J Immunol. 1990;20:1413–1416. - PubMed
-
- Yang YC, Ricciardi S, Ciarletta A, Calvetti J, Kelleher K, Clark SC. Expression cloning ofcDNA encoding a novel human hematopoietic growth factor: human homologue of murine T-cell growth factor P40. Blood. 1989;74:1880–1884. - PubMed
-
- Mock BA, Krall M, Kozak CA, Nesbitt MN, McBride OW, Renauld JC, Van Snick J. IL9 maps to mouse chromosome 13 and human chromosome 5. Immunogenetics. 1990;31:265–270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

