Glucocorticoids induce long-lasting effects in neural stem cells resulting in senescence-related alterations
- PMID: 21368868
- PMCID: PMC3032322
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2010.60
Glucocorticoids induce long-lasting effects in neural stem cells resulting in senescence-related alterations
Abstract
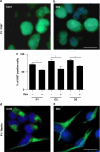
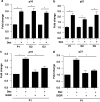
Alterations in intrauterine programming occurring during critical periods of development have adverse consequences for whole-organ systems or individual tissue functions in later life. In this paper, we show that rat embryonic neural stem cells (NSCs) exposed to the synthetic glucocorticoid dexamethasone (Dex) undergo heritable alterations, possibly through epigenetic mechanisms. Exposure to Dex results in decreased NSC proliferation, with no effects on survival or differentiation, and changes in the expression of genes associated with cellular senescence and mitochondrial functions. Dex upregulates cell cycle-related genes p16 and p21 in a glucocorticoid receptor(GR)-dependent manner. The senescence-associated markers high mobility group (Hmg) A1 and heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) are also upregulated in Dex-exposed NSCs, whereas Bmi1 (polycomb ring finger oncogene) and mitochondrial genes Nd3 (NADH dehydrogenase 3) and Cytb (cytochrome b) are downregulated. The concomitant decrease in global DNA methylation and DNA methyltransferases (Dnmts) suggests the occurrence of epigenetic changes. All these features are retained in daughter NSCs (never directly exposed to Dex) and are associated with a higher susceptibility to oxidative stress, as shown by the increased occurrence of apoptotic cell death on exposure to the redox-cycling reactive oxygen species (ROS) generator 2,3-dimethoxy-1-naphthoquinone (DMNQ). Our study provides novel evidence for programming effects induced by glucocorticoids (GCs) on NSCs and supports the idea that fetal exposure to endogenous or exogenous GCs is likely to result in long-term consequences that may predispose to neurodevelopmental and/or neurodegenerative disorders.
Figures
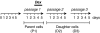


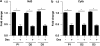
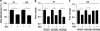
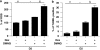
References
-
- Fowden AL, Forhead AJ. Endocrine mechanisms of intrauterine programming. Reproduction. 2004;127:515–526. - PubMed
-
- Barker DJ. Outcome of low birth weight. Horm Res. 1994;42:223–230. - PubMed
-
- Strang-Karlsson S, Räikkonen K, Pesonen AK, Kajantie E, Paavonen EJ, Lahti J, et al. Very low birth weight and behavioral symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in young adulthood: the Helsinki study of very-low-birth-weight adults. Am J Psychiatry. 2008;165:1345–1353. - PubMed
-
- Räikkönen K, Pesonen AK, Heinonen K, Kajantie E, Hovi P, Jarvenpaa AL, et al. Depression in young adults with very low birth weight: the Helsinki study of very low-birth-weight adults. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2008;65:290–296. - PubMed
-
- Seckl JR. Prenatal glucocorticoids and long-term programming. Eur J Endocrinol. 2004;151 (Suppl 3:U49–U62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

