MAGUKs, scaffolding proteins at cell junctions, are substrates of different proteases during apoptosis
- PMID: 21368887
- PMCID: PMC3077288
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2010.92
MAGUKs, scaffolding proteins at cell junctions, are substrates of different proteases during apoptosis
Abstract
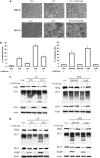
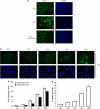
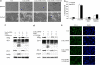
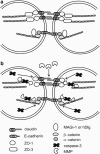
A major feature of apoptotic cell death is gross structural changes, one of which is the loss of cell-cell contacts. The caspases, executioners of apoptosis, were shown to cleave several proteins involved in the formation of cell junctions. The membrane-associated guanylate kinases (MAGUKs), which are typically associated with cell junctions, have a major role in the organization of protein-protein complexes at plasma membranes and are therefore potentially important caspase targets during apoptosis. We report here that MAGUKs are cleaved and/or degraded by executioner caspases, granzyme B and several cysteine cathepsins in vitro. When apoptosis was induced by UV-irradiation and staurosporine in different epithelial cell lines, caspases were found to efficiently cleave MAGUKs in these cell models, as the cleavages could be prevented by a pan-caspase inhibitor N-benzyloxycarbonyl-Val-Ala-Asp(OMe)fluoromethylketone. Using a selective lysosomal disrupting agent L-leucyl-L-leucine methyl ester, which induces apoptosis through the lysosomal pathway, it was further shown that MAGUKs are also cleaved by the cathepsins in HaCaT and CaCo-2 cells. Immunohistological data showed rapid loss of MAGUKs at the sites of cell-cell contacts, preceding actual cell detachment, suggesting that cleavage of MAGUKs is an important step in fast and efficient cell detachment.
Figures


Similar articles
-
hDLG/SAP97, a member of the MAGUK protein family, is a novel caspase target during cell-cell detachment in apoptosis.Biol Chem. 2005 Jul;386(7):705-10. doi: 10.1515/BC.2005.082. Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16207092
-
Cysteine cathepsins are not critical for TRAIL- and CD95-induced apoptosis in several human cancer cell lines.Biol Chem. 2012 Dec;393(12):1417-31. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2012-0213. Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23667901
-
Mechanisms of MAGUK-mediated cellular junctional complex organization.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2018 Feb;48:6-15. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2017.08.006. Epub 2017 Sep 14. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2018. PMID: 28917202 Review.
-
Cysteine cathepsins trigger caspase-dependent cell death through cleavage of bid and antiapoptotic Bcl-2 homologues.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jul 4;283(27):19140-50. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M802513200. Epub 2008 May 9. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18469004
-
Membrane-associated guanylate kinases regulate adhesion and plasticity at cell junctions.Annu Rev Biochem. 2005;74:219-45. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.74.082803.133339. Annu Rev Biochem. 2005. PMID: 15952887 Review.
Cited by
-
Fas activation alters tight junction proteins in acute lung injury.Thorax. 2019 Jan;74(1):69-82. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2018-211535. Epub 2018 Nov 1. Thorax. 2019. PMID: 30385692 Free PMC article.
-
The SF3B1R625H mutation promotes prolactinoma tumor progression through aberrant splicing of DLG1.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Jan 17;41(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02245-0. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35039052 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of the cell polarity determinant human Discs-large is a novel molecular marker of nodal involvement and poor prognosis in endometrial cancer.Br J Cancer. 2016 Apr 26;114(9):1012-8. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2016.24. Epub 2016 Mar 22. Br J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27002939 Free PMC article.
-
Increased activity of cell surface peptidases in HeLa cells undergoing UV-induced apoptosis is not mediated by caspase 3.Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(3):2650-2675. doi: 10.3390/ijms13032650. Epub 2012 Feb 28. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22489116 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of apoptosis methods recently used in Cancer Research and Cell Death & Disease publications.Cell Death Dis. 2012 Feb 2;3(2):e263. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2012.2. Cell Death Dis. 2012. PMID: 22297295 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Anderson JM. Cell signalling: MAGUK magic. Curr Biol. 1996;6:382–384. - PubMed
-
- Funke L, Dakoji S, Bredt DS. Membrane-associated guanylate kinases regulate adhesion and plasticity at cell junctions. Annu Rev Biochem. 2005;74:219–245. - PubMed
-
- Gonzales-Mariscal L, Betanzos A, Avila-Flores A. MAGUK proteins: structure and role in the tight junction. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2000;11:315–324. - PubMed
-
- Caruana G. Genetic studies define MAGUK proteins as regulators of epithelial cell polarity. Int J Dev Biol. 2002;46:511–518. - PubMed
-
- Hata Y, Nakanishi H, Takai Y. Synaptic PDZ domain-containing proteins. Neurosci Res. 1998;32:1–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

