Common structural traits for cystine knot domain of the TGFβ superfamily of proteins and three-fingered ectodomain of their cellular receptors
- PMID: 21369710
- PMCID: PMC11114550
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-011-0643-4
Common structural traits for cystine knot domain of the TGFβ superfamily of proteins and three-fingered ectodomain of their cellular receptors
Abstract
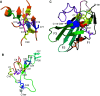
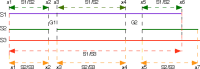
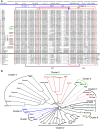
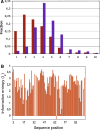
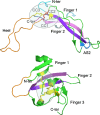
The transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ) superfamily of proteins and their receptors are crucial developmental factors for all metazoan organisms. Cystine-knot (CK) motif is a spatial feature of the TGFβ superfamily of proteins whereas the extra-cellular domains (ectodomains) of their respective receptors form three-fingered protein domain (TFPD), both stabilized by tight cystine networks. Analyses of multiple sequence alignments of these two domains encoded in various genomes revealed that the cystines forming the CK and TFPD folds are conserved, whereas the remaining polypeptide patches are diversified. Orthologues of the human TGFβs and their respective receptors expressed in diverse vertebrates retain high sequence conservation. Examination of 3D structures of various TGFβ factors bound to their receptors have revealed that the CK and TFPD domains display several similar spatial traits suggesting that these two different protein folds might have been acquired from a common ancestor.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Conserved structural determinants in three-fingered protein domains.FEBS J. 2008 Jun;275(12):3207-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06473.x. Epub 2008 May 13. FEBS J. 2008. PMID: 18485004
-
The three-fingered protein domain of the human genome.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008 Nov;65(21):3481-93. doi: 10.1007/s00018-008-8473-8. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008. PMID: 18821057 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution and classification of cystine knot-containing hormones and related extracellular signaling molecules.Mol Endocrinol. 2001 May;15(5):681-94. doi: 10.1210/mend.15.5.0639. Mol Endocrinol. 2001. PMID: 11328851 Review.
-
Identification of distinct inhibin and transforming growth factor beta-binding sites on betaglycan: functional separation of betaglycan co-receptor actions.J Biol Chem. 2006 Jun 23;281(25):17011-17022. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M601459200. Epub 2006 Apr 18. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16621788
-
A structural superfamily of growth factors containing a cystine knot motif.Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):421-4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90127-c. Cell. 1993. PMID: 8490958 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The role of FSH and TGF-β superfamily in follicle atresia.Aging (Albany NY). 2018 Mar 2;10(3):305-321. doi: 10.18632/aging.101391. Aging (Albany NY). 2018. PMID: 29500332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The regulation of TGF-β/SMAD signaling by protein deubiquitination.Protein Cell. 2014 Jul;5(7):503-17. doi: 10.1007/s13238-014-0058-8. Epub 2014 Apr 23. Protein Cell. 2014. PMID: 24756567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional diversity and pharmacological profiles of the FKBPs and their complexes with small natural ligands.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Sep;70(18):3243-75. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1206-z. Epub 2012 Dec 8. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23224428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Follistatin Forms a Stable Complex With Inhibin A That Does Not Interfere With Activin A Antagonism.Endocrinology. 2023 Jan 9;164(3):bqad017. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqad017. Endocrinology. 2023. PMID: 36718082 Free PMC article.
-
A daf-7-related TGF-β ligand (Hc-tgh-2) shows important regulations on the development of Haemonchus contortus.Parasit Vectors. 2020 Jun 26;13(1):326. doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-04196-x. Parasit Vectors. 2020. PMID: 32586367 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

