Effect of low dose exposure to the herbicide atrazine and its metabolite on cytochrome P450 aromatase and steroidogenic factor-1 mRNA levels in the brain of premetamorphic bullfrog tadpoles (Rana catesbeiana)
- PMID: 21371610
- PMCID: PMC3065035
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.12.019
Effect of low dose exposure to the herbicide atrazine and its metabolite on cytochrome P450 aromatase and steroidogenic factor-1 mRNA levels in the brain of premetamorphic bullfrog tadpoles (Rana catesbeiana)
Abstract
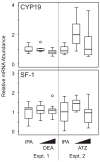
The transcriptional regulator steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1) and the enzyme cytochrome P450 aromatase (CYP19) play a central role in modulation of a broad range of tissue-specific developmental processes associated with hormone homeostasis that includes differentiation of the central nervous system. SF-1 and CYP19 expression may be targeted by a variety of endocrine disruptive agents prevalent within the environment. In the present study, we cloned and characterized partial sequences for bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana) SF-1 and CYP19 and examined the effects of a 48h exposure to 1 and 100μg/l of the herbicide atrazine (ATZ) and its major metabolite desethylatrazine (DEA), as well as 5ng/l of the estrogenic chemical, 17α-ethynylestradiol (EE(2)), and 673ng/l of the thyroid hormone, 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine (T(3)), on SF-1 and CYP19 mRNA abundance in the brains of premetamorphic bullfrog tadpoles. Quantitative RT-PCR analysis showed an increase in CYP19 mRNA following a 48h exposure to EE(2) but not T(3) while no significant changes in SF-1 transcript levels occurred. We observed a strong positive correlation between CYP19 and SF-1 transcript abundance in the ATZ-exposed animals which was not evident with DEA- or hormone-exposed tadpoles. Our results are intriguing in light of reported behavioral changes in ATZ-exposed frogs and suggest that further research is warranted to examine the relationship and role of CYP19 and SF-1 in amphibian brain development.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Altman J. Gonadal hormones humour the brain. Neuroendocrinol. 2004;79:287–295. - PubMed
-
- Coady KK, Murphy MB, Villeneuve DL, Hecker M, Jones PD, Carr JA, Solomon KR, Smith EE, Van der Kraak G, Kendall RJ, Giesy JP. Effects of atrazine on metamorphosis, growth, laryngeal and gonadal development, aromatase activity, and sex steroid concentrations in Xenopus laevis. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety. 2005;62:160–173. - PubMed
-
- Crews D, Fleming A, Willingham E, Baldwin R, Skipper JK. Role of steroidogenic factor I and aromatase in temperature-dependent sex determination in the red-eared slider turtle. J Exp Zool. 2001;290:597–606. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

