G4 motifs correlate with promoter-proximal transcriptional pausing in human genes
- PMID: 21371997
- PMCID: PMC3130262
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr079
G4 motifs correlate with promoter-proximal transcriptional pausing in human genes
Abstract
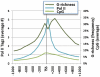
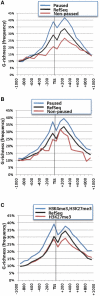
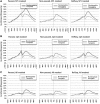
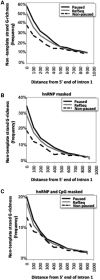
The RNA Pol II transcription complex pauses just downstream of the promoter in a significant fraction of human genes. The local features of genomic structure that contribute to pausing have not been defined. Here, we show that genes that pause are more G-rich within the region flanking the transcription start site (TSS) than RefSeq genes or non-paused genes. We show that enrichment of binding motifs for common transcription factors, such as SP1, may account for G-richness upstream but not downstream of the TSS. We further show that pausing correlates with the presence of a GrIn1 element, an element bearing one or more G4 motifs at the 5'-end of the first intron, on the non-template DNA strand. These results suggest potential roles for dynamic G4 DNA and G4 RNA structures in cis-regulation of pausing, and thus genome-wide regulation of gene expression, in human cells.
Figures

References
-
- Barski A, Cuddapah S, Cui K, Roh TY, Schones DE, Wang Z, Wei G, Chepelev I, Zhao K. High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell. 2007;129:823–837. - PubMed
-
- Margaritis T, Holstege FC. Poised RNA polymerase II gives pause for thought. Cell. 2008;133:581–584. - PubMed
-
- Gilmour DS. Promoter proximal pausing on genes in metazoans. Chromosoma. 2009;118:1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

