Effects of etanercept versus sulfasalazine in early axial spondyloarthritis on active inflammatory lesions as detected by whole-body MRI (ESTHER): a 48-week randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 21372193
- PMCID: PMC3211465
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2010.139667
Effects of etanercept versus sulfasalazine in early axial spondyloarthritis on active inflammatory lesions as detected by whole-body MRI (ESTHER): a 48-week randomised controlled trial
Erratum in
- Ann Rheum Dis. 2011 Jul;70(7):1350. Althoff, Ce [corrected to Althoff, C E]
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the potential of etanercept versus sulfasalazine to reduce active inflammatory lesions on whole-body MRI in active axial spondyloarthritis with a symptom duration of less than 5 years.
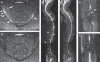
Methods: Patients were randomly assigned to etanercept (n=40) or sulfasalazine (n=36) treatment over 48 weeks. All patients showed active inflammatory lesions (bone marrow oedema) on MRI in either the sacroiliac joints or the spine. MRI was performed at weeks 0, 24 and 48 and was scored for active inflammatory lesions in sacroiliac joints and the spine including posterior segments and peripheral enthesitis by two radiologists, blinded for treatment arm and MRI time point.
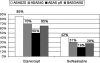
Results: In the etanercept group, the reduction of the sacroiliac joint score from 7.7 at baseline to 2.0 at week 48 was significantly (p=0.02) larger compared with the sulfasalazine group from 5.4 at baseline to 3.5 at week 48. A similar difference in the reduction of inflammation was found in the spine from 2.2 to 1.0 in the etanercept group versus from 1.4 to 1.3 in the sulfasalazine group between baseline and week 48, respectively (p=0.01). The number of enthesitic sites also improved significantly from 26 to 11 in the etanercept group versus 24 to 26 in the sulfasalazine group (p=0.04 for difference). 50% of patients reached clinical remission in the etanercept group versus 19% in the sulfasalazine group at week 48.
Conclusion: In patients with early axial spondyloarthritis active inflammatory lesions detected by whole-body MRI improved significantly more in etanercept versus sulfasalazine-treated patients. This effect correlated with a good clinical response in the etanercept group.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- van der Heijde D, Dijkmans B, Geusens P, et al. Efficacy and safety of infliximab in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: results of a randomized, placebo-controlled trial (ASSERT). Arthritis Rheum 2005;52:582–91 - PubMed
-
- Davis JC, Jr, Van Der Heijde D, Braun J, et al. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor receptor (etanercept) for treating ankylosing spondylitis: a randomized, controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 2003;48:3230–6 - PubMed
-
- van der Heijde D, Kivitz A, Schiff MH, et al. Efficacy and safety of adalimumab in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 2006;54:2136–46 - PubMed
-
- Braun J, Brandt J, Listing J, et al. Treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis with infliximab: a randomised controlled multicentre trial. Lancet 2002;359:1187–93 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

