(-)-Gossypol suppresses the growth of human prostate cancer xenografts via modulating VEGF signaling-mediated angiogenesis
- PMID: 21372225
- PMCID: PMC3227412
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0936
(-)-Gossypol suppresses the growth of human prostate cancer xenografts via modulating VEGF signaling-mediated angiogenesis
Abstract
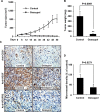
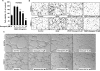
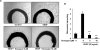
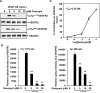
(-)-Gossypol, a natural BH3-mimetic and small-molecule Bcl-2 inhibitor, shows promise in ongoing phase II clinical trials for human cancers. However, whether (-)-gossypol plays functional roles in tumor angiogenesis has not been directly elucidated yet. In this study, we showed that (-)-gossypol dose dependently inhibited the expression of VEGF, Bcl-2, and Bcl-xL in human prostate cancer cells (PC-3 and DU 145) and primary cultured human umbilical vascular endothelial cells (HUVEC) in vitro. Notably, the growth of human prostate tumor PC-3 xenografts in mice was significantly suppressed by (-)-gossypol at a dosage of 15 mg/kg/d. This inhibitory action of (-)-gossypol in vivo was largely dependent on suppression of angiogenesis in the solid tumors, where VEGF expression and microvessel density were remarkably decreased. Furthermore, (-)-gossypol inhibited VEGF-induced chemotactic motility and tubulogenesis in HUVECs and human microvascular endothelial cells and suppressed microvessel sprouting from rat aortic rings ex vivo. When examined for the mechanism, we found that (-)-gossypol blocked the activation of VEGF receptor 2 kinase with the half maximal inhibitory concentration of 2.38 μmol/L in endothelial cells. Consequently, the phosphorylation of key intracellular proangiogenic kinases induced by VEGF was all suppressed by the treatment, such as Src family kinase, focal adhesion kinase, extracellular signal-related kinase, and AKT kinase. Taken together, the present study shows that (-)-gossypol potently inhibits human prostate tumor growth through modulating VEGF signaling pathway, which further validates its great potential in clinical practice.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid inhibits prostate tumor growth by suppressing vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2-mediated angiogenesis.Cancer Res. 2009 Jul 15;69(14):5893-900. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0755. Epub 2009 Jun 30. Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19567671 Free PMC article.
-
1'-Acetoxychavicol acetate suppresses angiogenesis-mediated human prostate tumor growth by targeting VEGF-mediated Src-FAK-Rho GTPase-signaling pathway.Carcinogenesis. 2011 Jun;32(6):904-12. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgr052. Epub 2011 Mar 22. Carcinogenesis. 2011. PMID: 21427164 Free PMC article.
-
Natural BH3 mimetic (-)-gossypol chemosensitizes human prostate cancer via Bcl-xL inhibition accompanied by increase of Puma and Noxa.Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Jul;7(7):2192-202. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0333. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008. PMID: 18645028 Free PMC article.
-
Antiangiogenic mechanisms of PJ-8, a novel inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling.Carcinogenesis. 2012 May;33(5):1022-30. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgs127. Epub 2012 Mar 20. Carcinogenesis. 2012. PMID: 22436611
-
Luteolin inhibits human prostate tumor growth by suppressing vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2-mediated angiogenesis.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52279. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052279. Epub 2012 Dec 31. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23300633 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparison of region-of-interest-averaged and pixel-averaged analysis of DCE-MRI data based on simulations and pre-clinical experiments.Phys Med Biol. 2017 Sep 5;62(18):N445-N459. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/aa84d6. Phys Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28786402 Free PMC article.
-
Plant Polyphenol Gossypol Induced Cell Death and Its Association with Gene Expression in Mouse Macrophages.Biomolecules. 2023 Mar 30;13(4):624. doi: 10.3390/biom13040624. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37189372 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitors of the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins: a patent review.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2012 Jan;22(1):37-55. doi: 10.1517/13543776.2012.644274. Epub 2011 Dec 23. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2012. PMID: 22195752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiogenesis inhibitors in cancer therapy: mechanistic perspective on classification and treatment rationales.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Oct;170(4):712-29. doi: 10.1111/bph.12344. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23962094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sequential treatment with AT-101 enhances cisplatin chemosensitivity in human non-small cell lung cancer cells through inhibition of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1-activated IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014 Dec 12;8:2517-29. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S71432. eCollection 2014. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014. PMID: 25548514 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N, Kerbel RS. Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target. Nature. 2005;438:967–74. - PubMed
-
- Albini A, Indraccolo S, Noonan DM, Pfeffer U. Functional genomics of endothelial cells treated with anti-angiogenic or angiopreventive drugs. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2010;27:419–39. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 2003;9:669–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

