Activation and function of the MAPKs and their substrates, the MAPK-activated protein kinases
- PMID: 21372320
- PMCID: PMC3063353
- DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.00031-10
Activation and function of the MAPKs and their substrates, the MAPK-activated protein kinases
Erratum in
- Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2012 Jun;76(2):496
Abstract
The mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) regulate diverse cellular programs by relaying extracellular signals to intracellular responses. In mammals, there are more than a dozen MAPK enzymes that coordinately regulate cell proliferation, differentiation, motility, and survival. The best known are the conventional MAPKs, which include the extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 (ERK1/2), c-Jun amino-terminal kinases 1 to 3 (JNK1 to -3), p38 (α, β, γ, and δ), and ERK5 families. There are additional, atypical MAPK enzymes, including ERK3/4, ERK7/8, and Nemo-like kinase (NLK), which have distinct regulation and functions. Together, the MAPKs regulate a large number of substrates, including members of a family of protein Ser/Thr kinases termed MAPK-activated protein kinases (MAPKAPKs). The MAPKAPKs are related enzymes that respond to extracellular stimulation through direct MAPK-dependent activation loop phosphorylation and kinase activation. There are five MAPKAPK subfamilies: the p90 ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK), the mitogen- and stress-activated kinase (MSK), the MAPK-interacting kinase (MNK), the MAPK-activated protein kinase 2/3 (MK2/3), and MK5 (also known as p38-regulated/activated protein kinase [PRAK]). These enzymes have diverse biological functions, including regulation of nucleosome and gene expression, mRNA stability and translation, and cell proliferation and survival. Here we review the mechanisms of MAPKAPK activation by the different MAPKs and discuss their physiological roles based on established substrates and recent discoveries.
Figures
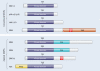
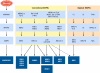
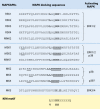
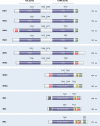


References
-
- Abe, M. K., et al. 2001. ERK7 is an autoactivated member of the MAPK family. J. Biol. Chem. 276:21272-21279. - PubMed
-
- Abe, M. K., et al. 2002. ERK8, a new member of the mitogen-activated protein kinase family. J. Biol. Chem. 277:16733-16743. - PubMed
-
- Aberg, E., et al. 2006. Regulation of MAPK-activated protein kinase 5 activity and subcellular localization by the atypical MAPK ERK4/MAPK4. J. Biol. Chem. 281:35499-35510. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

