Plasma biomarkers of oxidant stress and development of organ failure in severe sepsis
- PMID: 21372753
- PMCID: PMC3117035
- DOI: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e318217025a
Plasma biomarkers of oxidant stress and development of organ failure in severe sepsis
Abstract
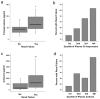
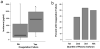
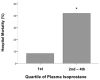
We hypothesized that circulating levels of lipid peroxidation products in patients with severe sepsis are associated with the development of pulmonary, renal, hepatic, circulatory, and coagulation failure. Plasma levels of F2-isoprostanes and isofurans were measured by mass spectroscopy on intensive care unit day 2 in 50 critically ill patients with severe sepsis. Plasma F2-isoprostane levels were higher in patients who developed renal failure compared with those who did not (65 pg/mL [interquartile range {IQR} 44-112] vs. 44 pg/mL [IQR 29-54], P = 0.009) as were isofuran levels (1,223 pg/mL [IQR 348-2,531] vs. 329 pg/mL [IQR 156-1,127], P = 0.009). Plasma F2-isoprostane levels were higher in patients who developed hepatic failure compared with those who did not (72 pg/mL [IQR 44-112] vs. 44 pg/mL [IQR 30-65], P = 0.023), and there was also a trend for higher isofuran levels (1,411 pg/mL [IQR 298-1,965] vs. 525 pg/mL [IQR 160-1,223], P = 0.14). Coagulation failure (thrombocytopenia) was associated with higher isofuran levels. Circulatory failure and acute lung injury were not associated with elevated levels of isoprostanes or isofurans. Patients with isoprostane levels above the 25th percentile had higher mortality (42%) compared with patients with levels below the 25th percentile (8%, P = 0.03). Plasma levels of F2-isoprostanes and isofurans are associated with renal, hepatic, and coagulation failure, but not with circulatory or pulmonary failure in severe sepsis, suggesting that lipid peroxidation is a prominent feature of septic multisystem organ failure. Plasma isoprostanes and isofurans may be useful for monitoring oxidative stress in treatment trials of antioxidant therapies in severe sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Disclosure: Dr. Ware has no conflicts of interest to disclose. Dr. Fessel has no conflicts of interest to disclose. Dr. May has no conflicts of interest to disclose. Dr. Roberts has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cell-free hemoglobin mediated oxidative stress is associated with acute kidney injury and renal replacement therapy in severe falciparum malaria: an observational study.BMC Infect Dis. 2017 Apr 27;17(1):313. doi: 10.1186/s12879-017-2373-1. BMC Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28449641 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between plasma lipid peroxidation products and primary graft dysfunction after lung transplantation is modified by donor smoking and reperfusion hyperoxia.J Heart Lung Transplant. 2016 Apr;35(4):500-507. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2015.12.012. Epub 2016 Jan 7. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2016. PMID: 26856667 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated Serum KIM-1 in Sepsis Correlates with Kidney Dysfunction and the Severity of Multi-Organ Critical Illness.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 27;25(11):5819. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115819. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892009 Free PMC article.
-
The biochemistry of the isoprostane, neuroprostane, and isofuran pathways of lipid peroxidation.Chem Phys Lipids. 2004 Mar;128(1-2):173-86. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2003.09.016. Chem Phys Lipids. 2004. PMID: 15037162 Review.
-
[Isoprostanes: new markers of oxidative stress in human diseases].Presse Med. 2000 Mar 25;29(11):604-10. Presse Med. 2000. PMID: 10776418 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Sustained high serum malondialdehyde levels are associated with severity and mortality in septic patients.Crit Care. 2013 Dec 11;17(6):R290. doi: 10.1186/cc13155. Crit Care. 2013. PMID: 24326199 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Role for Antioxidants in Acute Kidney Disease.Nutrients. 2017 Jul 7;9(7):718. doi: 10.3390/nu9070718. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28686196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of Post-critical Illness Cardiovascular Disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Jul 15;9:854421. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.854421. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35911546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin Therapy of Nondiabetic Septic Patients Is Predicted by para-Tyrosine/Phenylalanine Ratio and by Hydroxyl Radical-Derived Products of Phenylalanine.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:839748. doi: 10.1155/2015/839748. Epub 2015 Oct 20. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015. PMID: 26576228 Free PMC article.
-
Monitoring Severity of Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome: New Technologies.Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2017 Mar;18(3_suppl Suppl 1):S24-S31. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000001050. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2017. PMID: 28248831 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S, Moss M. The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1546–54. - PubMed
-
- Abraham E, Singer M. Mechanisms of sepsis-induced organ dysfunction. Crit Care Med. 2007;35:2408–16. - PubMed
-
- Montuschi P, Barnes P, Roberts LJ., 2nd Insights into oxidative stress: the isoprostanes. Curr Med Chem. 2007;14:703–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

