Therapeutic utility of phosphodiesterase type I inhibitors in neurological conditions
- PMID: 21373359
- PMCID: PMC3044262
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2011.00021
Therapeutic utility of phosphodiesterase type I inhibitors in neurological conditions
Abstract
Neuronal plasticity is an essential property of the brain that is impaired in different neurological conditions. Phosphodiesterase type 1 (PDE1) inhibitors can enhance levels of the second messengers cAMP/cGMP leading to the expression of neuronal plasticity-related genes, neurotrophic factors, and neuroprotective molecules. These neuronal plasticity enhancement properties make PDE1 inhibitors good candidates as therapeutic agents in many neurological conditions. However, the lack of specificity of the drugs currently available poses a challenge to the systematic evaluation of the beneficial effect of these agents. The development of more specific drugs may pave the way for the use of PDE1 inhibitors as therapeutic agents in cases of neurodevelopmental conditions such as fetal alcohol spectrum disorders and in degenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
Keywords: Alzheimer; Parkinson; cAMP; cGMP; drug development; fetal alcohol spectrum disorders; phosphodiesterase; vinpocetine.
Figures
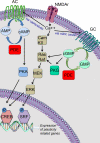
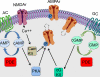
References
-
- Atkins C. M., Selcher J. C., Petraitis J. J., Trzaskos J. M., Sweatt J. D. (1998). The MAPK cascade is required for mammalian associative learning. Nat. Neurosci. 1, 602–609 - PubMed
-
- Bagetta V., Ghiglieri V., Sgobio C., Calabresi P., Picconi B. (2010). Synaptic dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 38, 493–497 - PubMed
-
- Barco A., Alaarcon J. M., Kandel E. (2002). Expression of constitutively active CREB protein facilitates the late phase of long-term potentiation by enhancing synaptic capture. Cell 35, 345–353 - PubMed
-
- Beavo J. A. (1995). Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: functional implications of multiple isoforms. Physiol. Rev. 75, 725–748 - PubMed
-
- Bereczki D., Fekete I. (2009). Vinpocetine for acute ischaemic stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 23, CD000480 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

