Auto-stimulatory action of secreted caveolin-1 on the proliferation of Ewing's sarcoma cells
- PMID: 21373757
- PMCID: PMC3335731
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2011.963
Auto-stimulatory action of secreted caveolin-1 on the proliferation of Ewing's sarcoma cells
Abstract
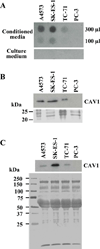
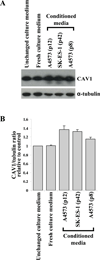
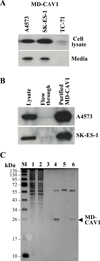
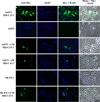
Caveolin-1 (CAV1) is highly expressed in Ewing's sarcoma (EWS). We previously showed that increased cellular CAV1 is associated with the regulation of the tumorigenicity, drug resistance and metastatic ability of EWS cells. Because several studies reported that melanoma and prostate cancer cells, which express relatively high CAV1 levels, secrete CAV1, and that secreted CAV1 is associated with tumor progression, our study explored the possibility that EWS cells also secreted CAV1 and that secreted CAV1 may contribute to EWS pathobiology. Results from experiments involving the ectopic expression of a Myc-tagged CAV1 protein in EWS cells as well as the supplementation of culture media with purified CAV1 protein followed by its intracellular localization using immunofluorescence demonstrated that EWS cells secrete CAV1, that they are able to take up the secreted protein, and that extracellular CAV1 enhances EWS cell proliferation. These findings strongly support the notion that secreted CAV1 may also contribute to the malignant properties of EWS.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Caveolin-1 (CAV1) is a target of EWS/FLI-1 and a key determinant of the oncogenic phenotype and tumorigenicity of Ewing's sarcoma cells.Cancer Res. 2006 Oct 15;66(20):9937-47. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0927. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 17047056
-
Caveolin-1 modulates the ability of Ewing's sarcoma to metastasize.Mol Cancer Res. 2010 Nov;8(11):1489-500. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-10-0060. Mol Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 21106507 Free PMC article.
-
EphA2-induced angiogenesis in ewing sarcoma cells works through bFGF production and is dependent on caveolin-1.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 12;8(8):e71449. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071449. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23951165 Free PMC article.
-
Promiscuous partnerships in Ewing's sarcoma.Cancer Genet. 2011 Jul;204(7):351-65. doi: 10.1016/j.cancergen.2011.07.008. Cancer Genet. 2011. PMID: 21872822 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Status of Proteomics in Ewing's Sarcoma.Proteomics Clin Appl. 2019 May;13(3):e1700130. doi: 10.1002/prca.201700130. Epub 2018 Aug 23. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2019. PMID: 29992772 Review.
Cited by
-
Caveolin-1 promotes Ewing sarcoma metastasis regulating MMP-9 expression through MAPK/ERK pathway.Oncotarget. 2016 Aug 30;7(35):56889-56903. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10872. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27487136 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolin-1 function at the plasma membrane and in intracellular compartments in cancer.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020 Jun;39(2):435-453. doi: 10.1007/s10555-020-09890-x. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020. PMID: 32458269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell Intrinsic and Extrinsic Mechanisms of Caveolin-1-Enhanced Metastasis.Biomolecules. 2019 Jul 29;9(8):314. doi: 10.3390/biom9080314. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31362353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial neural network inference (ANNI): a study on gene-gene interaction for biomarkers in childhood sarcomas.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 15;9(7):e102483. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102483. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25025207 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolin-1 in sarcomas: friend or foe?Oncotarget. 2011 Apr;2(4):305-12. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.255. Oncotarget. 2011. PMID: 21471610 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arndt CA, Crist WM. Common musculoskeletal tumors of childhood and adolescence. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:342–352. - PubMed
-
- Turc-Carel C, Aurias A, Mugneret F, et al. Chromosomes in Ewing's sarcoma. I. An evaluation of 85 cases of remarkable consistency of t(11;22)(q24;q12) Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1988;32:229–238. - PubMed
-
- Delattre O, Zucman J, Plougastel B, et al. Gene fusion with an ETS DNA-binding domain caused by chromosome translocation in human tumours. Nature. 1992;359:162–165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

