Occult and previous hepatitis B virus infection are not associated with hepatocellular carcinoma in United States patients with chronic hepatitis C
- PMID: 21374690
- PMCID: PMC3134544
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.24257
Occult and previous hepatitis B virus infection are not associated with hepatocellular carcinoma in United States patients with chronic hepatitis C
Abstract
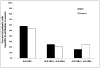
Previous studies have suggested that prior exposure to hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection may increase the risk of development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in patients with chronic hepatitis C. The aim of this study was to compare the prevalence of previous or occult HBV infection in a cohort of hepatitis B surface antigen-negative patients with histologically advanced chronic hepatitis C in the United States who did or did not develop HCC. Stored sera from 91 patients with HCC and 182 matched controls who participated in the Hepatitis C Antiviral Long-term Treatment against Cirrhosis (HALT-C) Trial were tested for hepatitis B core antibody (anti-HBc), hepatitis B surface antibody, and HBV DNA. Frozen liver samples from 28 HCC cases and 55 controls were tested for HBV DNA by way of real-time polymerase chain reaction. Anti-HBc (as a marker of previous HBV infection) was present in the serum of 41.8% HCC cases and 45.6% controls (P=0.54); anti-HBc alone was present in 16.5% of HCC cases and 24.7% of controls. HBV DNA was detected in the serum of only one control subject and no patients with HCC. HBV DNA (as a marker of occult HBV infection) was detected in the livers of 10.7% of HCC cases and 23.6% of controls (P=0.18).
Conclusion: Although almost half the patients in the HALT-C Trial had serological evidence of previous HBV infection, there was no difference in prevalence of anti-HBc in serum or HBV DNA in liver between patients who did or did not develop HCC. In the United States, neither previous nor occult HBV infection is an important factor in HCC development among patients with advanced chronic hepatitis C.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00006164.
Copyright © 2011 American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures
Comment in
-
Occult hepatitis B virus infection and hepatocellular carcinoma development in patients with chronic hepatitis C.Hepatology. 2011 Jul;54(1):373-4; author reply 374. doi: 10.1002/hep.24379. Hepatology. 2011. PMID: 21520203 No abstract available.
-
Occult hepatitis B virus infection: bit player or role player?Hepatology. 2011 Sep 2;54(3):760-3. doi: 10.1002/hep.24528. Hepatology. 2011. PMID: 21735471 No abstract available.
References
-
- Raimondo G, Allain JP, Brunetto MR, Buendia MA, Chen DS, Colombo M, et al. Statements from the Taormina expert meeting on occult hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 2008;49(4):652–7. - PubMed
-
- Torbenson M, Thomas DL. Occult hepatitis B. Lancet Infect Dis. 2002;2(8):479–86. - PubMed
-
- Brechot C, Thiers V, Kremsdorf D, Nalpas B, Pol S, Paterlini-Brechot P. Persistent hepatitis B virus infection in subjects without hepatitis B surface antigen: clinically significant or purely “occult”? [see comments] Hepatology. 2001;34(1):194–203. - PubMed
-
- Pollicino T, Squadrito G, Cerenzia G, Cacciola I, Raffa G, Craxi A, et al. Hepatitis B virus maintains its pro-oncogenic properties in the case of occult HBV infection. Gastroenterology. 2004;126(1):102–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- N01-DK-9-2325/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1 UL1 RR024986/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 1 UL1 RR025758-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2321/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1 UL1 RR024982-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2320/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR001066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000633/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000065/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024982/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2322/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000043/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2323/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000827/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024986/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR-00042/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 1 UL1 RR 025780-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR-00065/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2328/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2318/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2324/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2319/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR-00051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025780/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR-00827/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2327/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR-01066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR006192/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01 DK092323/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-DK-9-2326/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025758/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000042/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR-00633/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR-00043/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR-06192/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases