Avoidance perseveration during extinction training in Wistar-Kyoto rats: an interaction of innate vulnerability and stressor intensity
- PMID: 21376086
- PMCID: PMC3079807
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2011.02.029
Avoidance perseveration during extinction training in Wistar-Kyoto rats: an interaction of innate vulnerability and stressor intensity
Abstract
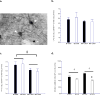
Given that avoidance is a core feature of anxiety disorders, Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) rats may be a good model of anxiety vulnerability for their hypersensitivity to stress and trait behavioral inhibition. Here, we examined the influence of strain and shock intensity on avoidance acquisition and extinction. Accordingly, we trained WKY and Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats in lever-press avoidance using either 1.0-mA or 2.0-mA foot-shock. After extinction, neuronal activation was visualized by c-Fos for overall activity and parvalbumin immunoreactivity for gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) neuron in brain areas linked to anxiety (medial prefrontal cortex and amygdala). Consistent with earlier work, WKY rats acquired lever-press avoidance faster and to a greater extent than SD rats. However, the intensity of foot shock did not differentially affect acquisition. Although there were no differences during extinction in SD rats, avoidance responses of WKY rats trained with the higher foot shock perseverated during extinction compared to those WKY rats trained with lower foot shock intensity or SD rats. WKY rats trained with 2.0-mA shock exhibited less GABAergic activation in the basolateral amygdala after extinction. These findings suggest that inhibitory modulation in amygdala is important to ensure successful extinction learning. Deficits in avoidance extinction secondary to lower GABAergic activation in baslolateral amygdala may contribute to anxiety vulnerability in this animal model of inhibited temperament.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Paired-housing selectively facilitates within-session extinction of avoidance behavior, and increases c-Fos expression in the medial prefrontal cortex, in anxiety vulnerable Wistar-Kyoto rats.Physiol Behav. 2016 Oct 1;164(Pt A):198-206. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2016.05.044. Epub 2016 May 24. Physiol Behav. 2016. PMID: 27235339
-
Dysfunction in amygdala-prefrontal plasticity and extinction-resistant avoidance: A model for anxiety disorder vulnerability.Exp Neurol. 2016 Jan;275 Pt 1(Pt 1):59-68. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.11.002. Epub 2015 Nov 4. Exp Neurol. 2016. PMID: 26546833 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and ΔFosB in emotion-associated neural circuitry after asymptotic levels of active avoidance behavior are attained.Brain Res Bull. 2013 Sep;98:102-10. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2013.07.004. Epub 2013 Aug 6. Brain Res Bull. 2013. PMID: 23932962
-
Rapid avoidance acquisition in Wistar-Kyoto rats.Behav Brain Res. 2008 Oct 10;192(2):191-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2008.04.006. Epub 2008 Apr 18. Behav Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18501974
-
The role of the medial prefrontal cortex-amygdala circuit in stress effects on the extinction of fear.Neural Plast. 2007;2007:30873. doi: 10.1155/2007/30873. Epub 2007 Jan 16. Neural Plast. 2007. PMID: 17502909 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibited Personality Temperaments Translated Through Enhanced Avoidance and Associative Learning Increase Vulnerability for PTSD.Front Psychol. 2019 Mar 22;10:496. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00496. eCollection 2019. Front Psychol. 2019. PMID: 30967806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of the hippocampus in avoidance learning and anxiety vulnerability.Front Behav Neurosci. 2014 Aug 8;8:273. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00273. eCollection 2014. Front Behav Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25152721 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of "Warm-Up" during Active Avoidance Learning in a Rat Model of Anxiety Vulnerability: Insights from Computational Modeling.Front Behav Neurosci. 2014 Aug 18;8:283. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00283. eCollection 2014. Front Behav Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25183956 Free PMC article.
-
Stress affects instrumental learning based on positive or negative reinforcement in interaction with personality in domestic horses.PLoS One. 2017 May 5;12(5):e0170783. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170783. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28475581 Free PMC article.
-
A Diet Enriched with Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus HN001 and Milk Fat Globule Membrane Alters the Gut Microbiota and Decreases Amygdala GABA a Receptor Expression in Stress-Sensitive Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 21;24(13):10433. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310433. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445611 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akirav I, Raizel H, Maroun M. Enhancement of conditioned fear extinction by infusion of the GABA(A) agonist muscimol into the rat prefrontal cortex and amygdala. Eur J Neurosci. 2006;23:758–764. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. DSM IV-Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Psychiatric Disorders. 4. American Psychiatric Association; Washington D.C: 1994.
-
- Beck KD, Jiao X, Pang KC, Servatius RJ. Vulnerability factors in anxiety determined through differences in active-avoidance behavior. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2010;34:852–860. - PubMed
-
- Berlau DJ, McGaugh JL. Enhancement of extinction memory consolidation: the role of the noradrenergic and GABAergic systems within the basolateral amygdala. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2006;86:123–132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

