Yap1 acts downstream of α-catenin to control epidermal proliferation
- PMID: 21376238
- PMCID: PMC3237196
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.031
Yap1 acts downstream of α-catenin to control epidermal proliferation
Abstract
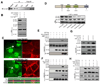
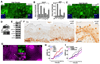
During development and regeneration, proliferation of tissue-specific stem cells is tightly controlled to produce organs of a predetermined size. The molecular determinants of this process remain poorly understood. Here, we investigate the function of Yap1, the transcriptional effector of the Hippo signaling pathway, in skin biology. Using gain- and loss-of-function studies, we show that Yap1 is a critical modulator of epidermal stem cell proliferation and tissue expansion. Yap1 mediates this effect through interaction with TEAD transcription factors. Additionally, our studies reveal that α-catenin, a molecule previously implicated in tumor suppression and cell density sensing in the skin, is an upstream negative regulator of Yap1. α-catenin controls Yap1 activity and phosphorylation by modulating its interaction with 14-3-3 and the PP2A phosphatase. Together, these data identify Yap1 as a determinant of the proliferative capacity of epidermal stem cells and as an important effector of a "crowd control" molecular circuitry in mammalian skin.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
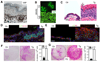
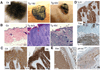
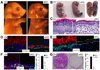
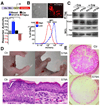
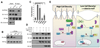
References
-
- Baumgartner R, Poernbacher I, Buser N, Hafen E, Stocker H. The WW domain protein Kibra acts upstream of Hippo in Drosophila. Dev Cell. 2010;18:309–316. - PubMed
-
- Camargo FD, Gokhale S, Johnnidis JB, Fu D, Bell GW, Jaenisch R, Brummelkamp TR. YAP1 increases organ size and expands undifferentiated progenitor cells. Curr Biol. 2007;17:2054–2060. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

