Estimating missing heritability for disease from genome-wide association studies
- PMID: 21376301
- PMCID: PMC3059431
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.02.002
Estimating missing heritability for disease from genome-wide association studies
Abstract
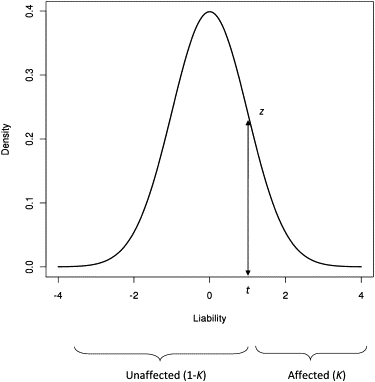
Genome-wide association studies are designed to discover SNPs that are associated with a complex trait. Employing strict significance thresholds when testing individual SNPs avoids false positives at the expense of increasing false negatives. Recently, we developed a method for quantitative traits that estimates the variation accounted for when fitting all SNPs simultaneously. Here we develop this method further for case-control studies. We use a linear mixed model for analysis of binary traits and transform the estimates to a liability scale by adjusting both for scale and for ascertainment of the case samples. We show by theory and simulation that the method is unbiased. We apply the method to data from the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium and show that a substantial proportion of variation in liability for Crohn disease, bipolar disorder, and type I diabetes is tagged by common SNPs.
Copyright © 2011 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Population structure can inflate SNP-based heritability estimates.Am J Hum Genet. 2011 Jul 15;89(1):191-3; author reply 193-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.05.025. Am J Hum Genet. 2011. PMID: 21763486 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Visscher P.M., Hill W.G., Wray N.R. Heritability in the genomics era—concepts and misconceptions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008;9:255–266. - PubMed
-
- Falconer D.S., Mackay T.F.C. Longman; Harlow, UK: 1996. Introduction to Quantitative Genetics.
-
- Lynch M., Walsh B. Sinauer Associates; Sunderland: 1998. Genetics and Analysis of Quantitative Traits.
-
- Patterson H.D., Thompson R. Recovery of interblock information when block sizes are unequal. Biometrika. 1971;58:545–554.
-
- Henderson C.R. University of Guelph; Guelph, Canada: 1984. Applications of Linear Models in Animal Breeding.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources