Drug tolerance in replicating mycobacteria mediated by a macrophage-induced efflux mechanism
- PMID: 21376383
- PMCID: PMC3117281
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.022
Drug tolerance in replicating mycobacteria mediated by a macrophage-induced efflux mechanism
Erratum in
- Cell. 2011 Apr 1;145(1):159
Abstract
Treatment of tuberculosis, a complex granulomatous disease, requires long-term multidrug therapy to overcome tolerance, an epigenetic drug resistance that is widely attributed to nonreplicating bacterial subpopulations. Here, we deploy Mycobacterium marinum-infected zebrafish larvae for in vivo characterization of antitubercular drug activity and tolerance. We describe the existence of multidrug-tolerant organisms that arise within days of infection, are enriched in the replicating intracellular population, and are amplified and disseminated by the tuberculous granuloma. Bacterial efflux pumps that are required for intracellular growth mediate this macrophage-induced tolerance. This tolerant population also develops when Mycobacterium tuberculosis infects cultured macrophages, suggesting that it contributes to the burden of drug tolerance in human tuberculosis. Efflux pump inhibitors like verapamil reduce this tolerance. Thus, the addition of this currently approved drug or more specific efflux pump inhibitors to standard antitubercular therapy should shorten the duration of curative treatment.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

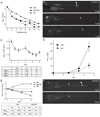


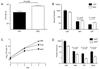
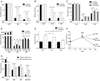

Comment in
-
Directly observing therapy: a new view of drug tolerance in tuberculosis.Cell. 2011 Apr 1;145(1):13-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.041. Cell. 2011. PMID: 21458661
References
-
- Akira M, Sakatani M, Ishikawa H. Transient radiographic progression during initial treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis: CT findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2000;24:426–431. - PubMed
-
- Amaral L, Martins M, Viveiros M. Enhanced killing of intracellular multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis by compounds that affect the activity of efflux pumps. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007;59:1237–1246. - PubMed
-
- Aubry A, Chosidow O, Caumes E, Robert J, Cambau E. Sixty-three cases of Mycobacterium marinum infection: clinical features, treatment, and antibiotic susceptibility of causative isolates. Arch Intern Med. 2002;162:1746–1752. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U54 AI057141/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI54503/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI030036/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5R21AI078189-02/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI078189/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI073328/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI036396/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 MH099901/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI054503/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5R21 AI073328-02/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U54AI057141/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI55396/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI055396/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI076620/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

