Adults with a family history of alcohol related problems are more impulsive on measures of response initiation and response inhibition
- PMID: 21376480
- PMCID: PMC3137712
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2011.02.001
Adults with a family history of alcohol related problems are more impulsive on measures of response initiation and response inhibition
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have found individuals with family histories of alcohol use disorders are more impulsive on some but not all laboratory behavioral measures, suggesting deficits on specific forms of impulse control. However, drawing conclusions is tenuous because these different measures have not been administered together in the same group of participants.
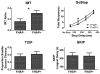
Methods: In the present study, we compared healthy 21-35 year old adults with family histories of alcohol related problems (FHAP+) or without such histories (FHAP-) on behavioral measures of response inhibition, response initiation, and consequence sensitivity impulsivity. FHAP+ (n=36) and FHAP- (n=36) participants were compared on performance on the Immediate Memory Task (IMT, response initiation), GoStop Impulsivity Paradigm (GoStop, response inhibition), Two Choice Impulsivity Paradigm (TCIP, consequence sensitivity) and Single Key Impulsivity Paradigm (SKIP, consequence sensitivity).
Results: FHAP+ individuals were more impulsive on the IMT and GoStop but not on the TCIP or SKIP.
Conclusions: These results suggest that response initiation and response inhibition impulsivity are increased in individuals with family histories of alcohol related problems despite not having alcohol or drug use disorders themselves. In contrast, increased consequence sensitivity impulsivity may be associated with additional risk factors such as more severe family histories of alcohol use disorders, or it may be increased as a consequence of heavy drug or alcohol use.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Acheson A, Robinson JL, Glahn DC, Lovallo WR, Fox PT. Differential activation of the anterior cingulate cortex and caudate nucleus during a gambling simulation in persons with a family history of alcoholism: studies from the Oklahoma Family Health Patterns Project. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2009;100:17–23. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bechara A, Van Der Linden M. Decision-making and impulse control after frontal lobe injuries. Curr Opin Neurol. 2005;18:734–739. - PubMed
-
- Billieux J, Gay P, Rochat L, Van der Linden M. The role of urgency and its underlying psychological mechanisms in problematic behaviours. Behav Res Ther. 2010;48:1085–1096. - PubMed
-
- Bornovalova MA, Lejuez CW, Daughters SB, Zachary Rosenthal M, Lynch TR. Impulsivity as a common process across borderline personality and substance use disorders. Clin Psych Rev. 2005;25:790–812. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DA026868/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA014988/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA012046/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000149/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 RR025766/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AA12046/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- T32-AA00765/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AA014988/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR000118/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- KL2-RR025766/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA026868/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025767/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

