The role of GABA in human motor learning
- PMID: 21376596
- PMCID: PMC3063350
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.01.069
The role of GABA in human motor learning
Abstract
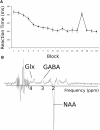
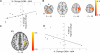
GABA modification plays an important role in motor cortical plasticity. We therefore hypothesized that interindividual variation in the responsiveness of the GABA system to modification influences learning capacity in healthy adults. We assessed GABA responsiveness by transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), an intervention known to decrease GABA. The magnitude of M1 GABA decrease induced by anodal tDCS correlated positively with both the degree of motor learning and the degree of fMRI signal change within the left M1 during learning. This study therefore suggests that the responsiveness of the GABAergic system to modification may be relevant to short-term motor learning behavior and learning-related brain activity.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
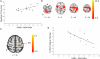
References
-
- Ziemann U., Muellbacher W., Hallett M., Cohen L.G. Modulation of practice-dependent plasticity in human motor cortex. Brain. 2001;124:1171–1181. - PubMed
-
- Tegenthoff M., Witscher K., Schwenkreis P., Liepert J. Pharmacological modulation of training-induced plastic changes in human motor cortex. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. Suppl. 1999;51:188–196. - PubMed
-
- Floyer-Lea A., Wylezinska M., Kincses T., Matthews P.M. Rapid modulation of GABA concentration in human sensorimotor cortex during motor learning. J. Neurophysiol. 2006;95:1639–1644. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

