Risk factors for failed staged palliation after bidirectional Glenn in infants who have undergone stage one palliation
- PMID: 21377892
- PMCID: PMC3376531
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejcts.2011.01.056
Risk factors for failed staged palliation after bidirectional Glenn in infants who have undergone stage one palliation
Abstract
Objective: The bidirectional Glenn procedure (BDG) is a routine intermediary step in single-ventricle palliation. In this study, we examined risk factors for death or transplant and failure to reach Fontan completion after BDG in patients, who had previously undergone stage one palliation (S1P).
Methods: All patients at our institution, who underwent BDG following S1P between 2002 and 2009 (n=194), were included in the analysis.
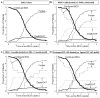
Results: Transplant-free survival through 18 months post BDG was 91%. Univariable competing risk analyses showed atrioventricular valve regurgitation (AVVR) >mild, age ≤ 3 months at BDG, ventricular dysfunction >mild, and prolonged hospital stay after S1P to be associated with increased risk of death or orthotopic heart transplant. Multivariable competing risk analysis through 5 years of follow-up showed >mild AVVR (hazard ratio (HR) 7.5, 95% confidence interval (CI) 3.0-18.8), prolonged hospitalization after S1P (HR 4.5, 95% CI 1.8-11.5), and age ≤ 3 months at BDG (HR 6.8, 95% CI 2.3-20.0) to be independent risk factors for death or transplant. Concomitantly, > mild AVVR and age ≤ 3 months were independently associated with an overall decreased rate of Fontan completion.
Conclusions: Pre-BDG AVVR, age ≤ 3 months at time of BDG, and prolonged hospitalization after S1P are independently associated with decreased successful progression of staged palliation in midterm follow-up after BDG.
Copyright © 2011 European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Bridges ND, Jonas RA, Mayer JE, Flanagan MF, Keane JF, Castaneda AR. Bidirectional cavopulmonary anastomosis as interim palliation for high-risk Fontan candidates. Early results. Circulation. 1990;82:IV170–6. - PubMed
-
- Hawkins JA, Shaddy RE, Day RW, Sturtevant JE, Orsmond GS, McGough EC. Mid-term results after bidirectional cavopulmonary shunts. Ann Thorac Surg. 1993;56:833–7. - PubMed
-
- Jonas RA. Indications and timing for the bidirectional Glenn shunt versus the fenestrated Fontan circulation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1994;108:522–4. - PubMed
-
- Lai L, Laussen PC, Cua CL, Wessel DL, Costello JM, del Nido PJ, Mayer JE, Thiagarajan RR. Outcomes after bidirectional Glenn operation: Blalock-Taussig shunt versus right ventricle-to-pulmonary artery conduit. Ann Thorac Surg. 2007;83:1768–73. - PubMed
-
- Scheurer MA, Hill EG, Vasuki N, Maurer S, Graham EM, Bandisode V, Shirali GS, Atz AM, Bradley SM. Survival after bidirectional cavopulmonary anastomosis: analysis of preoperative risk factors. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007;134:82–9. - PubMed

