A role for decorin in a murine model of allergen-induced asthma
- PMID: 21378022
- PMCID: PMC5243205
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00300.2009
A role for decorin in a murine model of allergen-induced asthma
Abstract
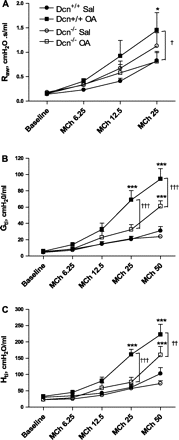
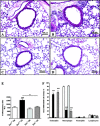
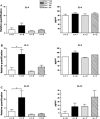
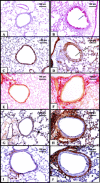
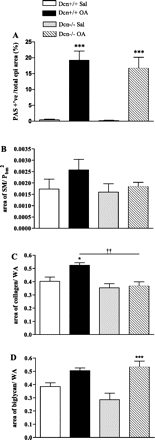
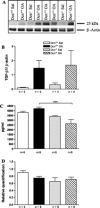
Decorin (Dcn) is an extracellular matrix proteoglycan, which affects airway mechanics, airway-parenchymal interdependence, airway smooth muscle proliferation and apoptosis, and transforming growth factor-β bioavailability. As Dcn deposition is differentially altered in asthma, we questioned whether Dcn deficiency would impact the development of allergen-induced asthma in a mouse model. Dcn(-/-) and Dcn(+/+) mice (C57Bl/6) were sensitized with ovalbumin (OA) and challenged intranasally 3 days/wk × 3 wk. After OA challenge, mice were anesthetized, and respiratory mechanics measured under baseline conditions and after delivery of increasing concentrations of methacholine aerosol. Complex impedance was partitioned into airway resistance and tissue elastance and damping. Bronchoalveolar lavage was performed. Lungs were excised, and tissue sections evaluated for inflammatory cell influx, α-smooth muscle actin, collagen, biglycan, and Dcn deposition. Changes in TH-2 cytokine mRNA and protein were also measured. Airway resistance was increased in OA-challenged Dcn(+/+) mice only (P < 0.05), whereas tissue elastance and damping were increased in both OA-challenged Dcn(+/+) and Dcn(-/-), but more so in Dcn(+/+) mice (P < 0.001). Inflammation and collagen staining within the airway wall were increased with OA in Dcn(+/+) only (P < 0.001 and P < 0.01, respectively, vs. saline). IL-5 and IL-13 mRNA were increased in lung tissue of OA-challenged Dcn(+/+) mice. Dcn deficiency resulted in more modest OA-induced hyperresponsiveness, evident at the level of the central airways and distal lung. Differences in physiology were accompanied by differences in inflammation and remodeling. These findings may be, in part, due to the well-described ability of Dcn to bind transforming growth factor-β and render it less bioavailable.
Figures

References
-
- Al JR, Roughley PJ, Ludwig MS. Effect of glycosaminoglycan degradation on lung tissue viscoelasticity. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 280: L306–L315, 2001. - PubMed
-
- Busse WW. Leukotrienes and inflammation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 157: S210–S213, 1998. - PubMed
-
- Cavalcante FS, Ito S, Brewer K, Sakai H, Alencar AM, Almeida MP, Andrade JS, Jr, Majumdar A, Ingenito EP, Suki B. Mechanical interactions between collagen and proteoglycans: implications for the stability of lung tissue. J Appl Physiol 98: 672–679, 2005. - PubMed
-
- D'Antoni ML, Torregiani C, Ferraro P, Michoud MC, Mazer B, Martin JG, Ludwig MS. Effects of decorin and biglycan on human airway smooth muscle cell proliferation and apoptosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 294: L764–L771, 2008. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

