Generation and screening of Pichia pastoris strains with enhanced protein production by use of microengraving
- PMID: 21378037
- PMCID: PMC3126391
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00104-11
Generation and screening of Pichia pastoris strains with enhanced protein production by use of microengraving
Abstract
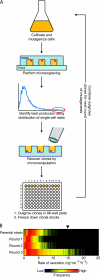
The selection of highly productive cell lines remains a key step for manufacturing therapeutic proteins. Microengraving was used to screen chemically mutagenized populations of Pichia pastoris for increased production of an Fc fragment. Clones retrieved following three rounds of mutagenesis yielded titers 2.65-fold greater than those of the parental strain.
Figures
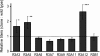
References
-
- Browne S. M., Al-Rubeai M. 2007. Selection methods for high-producing mammalian cell lines. Trends Biotechnol. 25:425–432 - PubMed
-
- Cereghino J. L., Cregg J. M. 2000. Heterologous protein expression in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 24:45–66 - PubMed
-
- Farid S. S. 2007. Process economics of industrial monoclonal antibody manufacture. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 848:8–18 - PubMed
-
- Li P. Z., et al. 2007. Expression of recombinant proteins in Pichia pastoris. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 142:105–124 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

