Novel type II anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (GA101) evokes homotypic adhesion and actin-dependent, lysosome-mediated cell death in B-cell malignancies
- PMID: 21378274
- PMCID: PMC3099571
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-07-296913
Novel type II anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (GA101) evokes homotypic adhesion and actin-dependent, lysosome-mediated cell death in B-cell malignancies
Abstract
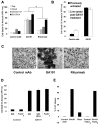
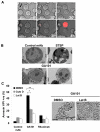
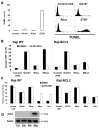
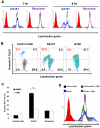
The anti-CD20 mAb rituximab has substantially improved the clinical outcome of patients with a wide range of B-cell malignancies. However, many patients relapse or fail to respond to rituximab, and thus there is intense investigation into the development of novel anti-CD20 mAbs with improved therapeutic efficacy. Although Fc-FcγR interactions appear to underlie much of the therapeutic success with rituximab, certain type II anti-CD20 mAbs efficiently induce programmed cell death (PCD), whereas rituximab-like type I anti-CD20 mAbs do not. Here, we show that the humanized, glycoengineered anti-CD20 mAb GA101 and derivatives harboring non-glycoengineered Fc regions are type II mAb that trigger nonapoptotic PCD in a range of B-lymphoma cell lines and primary B-cell malignancies. We demonstrate that GA101-induced cell death is dependent on actin reorganization, can be abrogated by inhibitors of actin polymerization, and is independent of BCL-2 overexpression and caspase activation. GA101-induced PCD is executed by lysosomes which disperse their contents into the cytoplasm and surrounding environment. Taken together, these findings reveal that GA101 is able to potently elicit actin-dependent, lysosomal cell death, which may potentially lead to improved clearance of B-cell malignancies in vivo.
Figures


References
-
- Coiffier B, Lepage E, Briere J, et al. CHOP Chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CHOP alone in elderly patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(4):235–242. - PubMed
-
- Schulz H, Bohlius JF, Trelle S, et al. Immunochemotherapy with rituximab and overall survival in patients with indolent or mantle cell lymphoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007;99(9):706–714. - PubMed
-
- Hallek M, Fischer K, Fingerle-Rowson G, et al. Addition of rituximab to fludarabine and cyclophosphamide in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2010;376(9747):1164–1174. - PubMed
-
- van Meerten T, Hagenbeek A. CD20-targeted therapy: the next generation of antibodies. Semin Hematol. 2010;47(2):199–210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

