Rapid three-dimensional isotropic imaging of living cells using Bessel beam plane illumination
- PMID: 21378978
- PMCID: PMC3626440
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.1586
Rapid three-dimensional isotropic imaging of living cells using Bessel beam plane illumination
Abstract
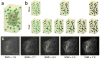
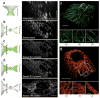
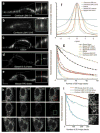
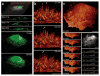
A key challenge when imaging living cells is how to noninvasively extract the most spatiotemporal information possible. Unlike popular wide-field and confocal methods, plane-illumination microscopy limits excitation to the information-rich vicinity of the focal plane, providing effective optical sectioning and high speed while minimizing out-of-focus background and premature photobleaching. Here we used scanned Bessel beams in conjunction with structured illumination and/or two-photon excitation to create thinner light sheets (<0.5 μm) better suited to three-dimensional (3D) subcellular imaging. As demonstrated by imaging the dynamics of mitochondria, filopodia, membrane ruffles, intracellular vesicles and mitotic chromosomes in live cells, the microscope currently offers 3D isotropic resolution down to ∼0.3 μm, speeds up to nearly 200 image planes per second and the ability to noninvasively acquire hundreds of 3D data volumes from single living cells encompassing tens of thousands of image frames.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Bessel beams beyond the limit.Nat Methods. 2013 Feb;10(2):102-3. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2354. Nat Methods. 2013. PMID: 23479799 No abstract available.
References
-
- Toomre D, Pawley JB. Disk-scanning confocal microscopy. In: Pawley JB, editor. Handbook of Biological Confocal Microscopy. 3. Springer; New York: 2006. pp. 221–238.
-
- Zimmermann T, Rietdorf J, Pepperkok R. Spectral imaging and its applications in live cell microscopy. FEBS Lett. 2003;546:87–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

