Simultaneous determination of alfentanil and midazolam in human plasma using liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry
- PMID: 21382685
- PMCID: PMC3089954
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpba.2011.01.040
Simultaneous determination of alfentanil and midazolam in human plasma using liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry
Abstract
A fast, sensitive and selective liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method for the determination of alfentanil and midazolam in human plasma has been developed and validated. Alfentanil and midazolam were extracted from plasma using a mixed-mode cation exchange solid phase extraction method, with recoveries of both compounds greater than 80% at 3 different concentrations (1, 10 and 100ng/ml). Compounds were analyzed on a C(18) column with a water and methanol mobile phase gradient with acetic acid as an additive, at a flow rate of 0.3ml/min. The working assay range was linear from 0.25 to 100ng/ml for each compound. The signal to noise ratio was 80 and 40 for alfentanil and midazolam, respectively, at the lowest concentration calibration standard, with less than 10% matrix suppression by human plasma at this concentration. Alfentanil and midazolam were stable in human plasma during storage at -80°C, processing, and analysis. The procedure was validated and applied to the analysis of plasma samples from healthy human subjects administered oral and intravenous alfentanil and midazolam.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: No author has any conflict of interest
Figures
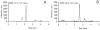



References
-
- Shimada T, Yamazaki H, Mimura M, Inui Y, Guengerich FP. Interindividual variations in human liver cytochrome P-450 enzymes involved in the oxidation of drugs, carcinogens and toxic chemicals: Studies with liver microsomes of 30 Japanese and 30 Caucasians. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994;270:414–423. - PubMed
-
- Wilkinson GR. Drug metabolism and variability among patients in drug response. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:2211–2221. - PubMed
-
- Plant N. The human cytochrome P450 sub-family: transcriptional regulation, inter-individual variation and interaction networks. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1770:478–488. - PubMed
-
- Harris R, Jang G, Tsunoda S. Dietary effects on drug metabolism and transport. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2003;42:1071–1088. - PubMed
-
- Streetman DS, Bertino JS, Jr, Nafziger AN. Phenotyping of drug-metabolizing enzymes in adults: a review of in-vivo cytochrome P450 phenotyping probes. Pharmacogenetics. 2000;10:187–216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

