On emerging nuclear order
- PMID: 21383074
- PMCID: PMC3051810
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201010129
On emerging nuclear order
Abstract
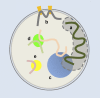
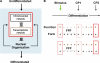
Although the nonrandom nature of interphase chromosome arrangement is widely accepted, how nuclear organization relates to genomic function remains unclear. Nuclear subcompartments may play a role by offering rich microenvironments that regulate chromatin state and ensure optimal transcriptional efficiency. Technological advances now provide genome-wide and four-dimensional analyses, permitting global characterizations of nuclear order. These approaches will help uncover how seemingly separate nuclear processes may be coupled and aid in the effort to understand the role of nuclear organization in development and disease.
Figures

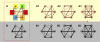
References
-
- Albiez H., Cremer M., Tiberi C., Vecchio L., Schermelleh L., Dittrich S., Küpper K., Joffe B., Thormeyer T., von Hase J., et al. 2006. Chromatin domains and the interchromatin compartment form structurally defined and functionally interacting nuclear networks. Chromosome Res. 14:707–733 10.1007/s10577-006-1086-x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

