Reversible inhibitor of p97, DBeQ, impairs both ubiquitin-dependent and autophagic protein clearance pathways
- PMID: 21383145
- PMCID: PMC3064330
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1015312108
Reversible inhibitor of p97, DBeQ, impairs both ubiquitin-dependent and autophagic protein clearance pathways
Abstract
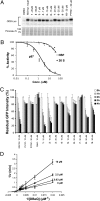
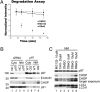
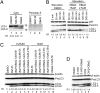
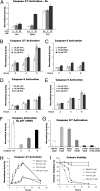
A specific small-molecule inhibitor of p97 would provide an important tool to investigate diverse functions of this essential ATPase associated with diverse cellular activities (AAA) ATPase and to evaluate its potential to be a therapeutic target in human disease. We carried out a high-throughput screen to identify inhibitors of p97 ATPase activity. Dual-reporter cell lines that simultaneously express p97-dependent and p97-independent proteasome substrates were used to stratify inhibitors that emerged from the screen. N2,N4-dibenzylquinazoline-2,4-diamine (DBeQ) was identified as a selective, potent, reversible, and ATP-competitive p97 inhibitor. DBeQ blocks multiple processes that have been shown by RNAi to depend on p97, including degradation of ubiquitin fusion degradation and endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation pathway reporters, as well as autophagosome maturation. DBeQ also potently inhibits cancer cell growth and is more rapid than a proteasome inhibitor at mobilizing the executioner caspases-3 and -7. Our results provide a rationale for targeting p97 in cancer therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Giaever G, et al. Functional profiling of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome. Nature. 2002;418:387–391. - PubMed
-
- Müller JM, Deinhardt K, Rosewell I, Warren G, Shima DT. Targeted deletion of p97 (VCP/CDC48) in mouse results in early embryonic lethality. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;354:459–465. - PubMed
-
- Golbik R, Lupas AN, Koretke KK, Baumeister W, Peters J. The Janus face of the archaeal Cdc48/p97 homologue VAT: protein folding versus unfolding. Biol Chem. 1999;380:1049–1062. - PubMed
-
- Rabouille C, Levine TP, Peters JM, Warren G. An NSF-like ATPase, p97, and NSF mediate cisternal regrowth from mitotic Golgi fragments. Cell. 1995;82:905–914. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

