Mutated beta-catenin evades a microRNA-dependent regulatory loop
- PMID: 21383185
- PMCID: PMC3064338
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1101734108
Mutated beta-catenin evades a microRNA-dependent regulatory loop
Abstract
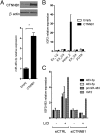
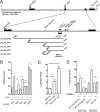
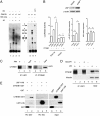
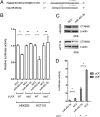
hsa-mir-483 is located within intron 2 of the IGF2 gene. We have previously shown oncogenic features of miR-483-3p through cooperation with IGF2 or by independently targeting the proapoptotic gene BBC3/PUMA. Here we demonstrate that expression of miR-483 can be induced independently of IGF2 by the oncoprotein β-catenin through an interaction with the basic helix-loop-helix protein upstream stimulatory transcription factor 1. We also show that β-catenin itself is a target of miR-483-3p, triggering a negative regulatory loop that becomes ineffective in cells harboring an activating mutation of β-catenin. These results provide insights into the complex regulation of the IGF2/miR-483 locus, revealing players in the β-catenin pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Perez-Moreno M, Jamora C, Fuchs E. Sticky business: Orchestrating cellular signals at adherens junctions. Cell. 2003;112:535–548. - PubMed
-
- Clevers H. Wnt/β-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell. 2006;127:469–480. - PubMed
-
- Wang SS, et al. Alterations of the PPP2R1B gene in human lung and colon cancer. Science. 1998;282:284–287. - PubMed
-
- Satoh S, et al. AXIN1 mutations in hepatocellular carcinomas, and growth suppression in cancer cells by virus-mediated transfer of AXIN1. Nat Genet. 2000;24:245–250. - PubMed
-
- Major MB, et al. Wilms tumor suppressor WTX negatively regulates WNT/β-catenin signaling. Science. 2007;316:1043–1046. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

