Inflammation-dependent secretion and splicing of IL-32{gamma} in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 21383200
- PMCID: PMC3064318
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1016005108
Inflammation-dependent secretion and splicing of IL-32{gamma} in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
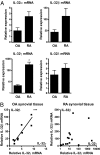
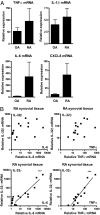
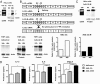
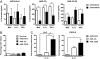
Different splice variants of the proinflammatory cytokine IL-32 are found in various tissues; their putative differences in biological function remain unknown. In the present study, we report that IL-32γ is the most active isoform of the cytokine. Splicing to one less active IL-32β appears to be a salvage mechanism to reduce inflammation. Adenoviral overexpression of IL-32γ (AdIL-32γ) resulted in exclusion of the IL-32γ-specific exon in vitro as well as in vivo, primarily leading to expression of IL-32β mRNA and protein. Splicing of the IL-32γ-specific exon was prevented by single-nucleotide mutation, which blocked recognition of the splice site by the spliceosome. Overexpression of splice-resistant IL-32γ in THP1 cells or rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovial fibroblasts resulted in a greater induction of proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β, compared with IL-32β. Intraarticular introduction of IL-32γ in mice resulted in joint inflammation and induction of several mediators associated with joint destruction. In RA synovial fibroblasts, overexpression of primarily IL-32β showed minimal secretion and reduced cytokine production. In contrast, overexpression of splice-resistant IL-32γ in RA synovial fibroblasts exhibited marked secretion of IL-32γ. In RA, we observed increased IL-32γ expression compared with osteoarthritis synovial tissue. Furthermore, expression of TNFα and IL-6 correlated significantly with IL-32γ expression in RA, whereas this was not observed for IL-32β. These data reveal that naturally occurring IL-32γ can be spliced into IL-32β, which is a less potent proinflammatory mediator. Splicing of IL-32γ into IL-32β is a safety switch in controlling the effects of IL-32γ and thereby reduces chronic inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Goda C, et al. Involvement of IL-32 in activation-induced cell death in T cells. Int Immunol. 2006;18:233–240. - PubMed
-
- Kim SH, Han SY, Azam T, Yoon DY, Dinarello CA. Interleukin-32: A cytokine and inducer of TNFα. Immunity. 2005;22:131–142. - PubMed
-
- Dahl CA, Schall RP, He HL, Cairns JS. Identification of a novel gene expressed in activated natural killer cells and T cells. J Immunol. 1992;148:597–603. - PubMed
-
- Mun SH, et al. Tumor necrosis factor α-induced interleukin-32 is positively regulated via the Syk/protein kinase Cδ/JNK pathway in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60:678–685. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

