Peripheral calcium-permeable AMPA receptors regulate chronic inflammatory pain in mice
- PMID: 21383497
- PMCID: PMC3069784
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI44911
Peripheral calcium-permeable AMPA receptors regulate chronic inflammatory pain in mice
Abstract
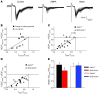
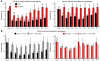
α-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid-type (AMPA-type) glutamate receptors (AMPARs) play an important role in plasticity at central synapses. Although there is anatomical evidence for AMPAR expression in the peripheral nervous system, the functional role of such receptors in vivo is not clear. To address this issue, we generated mice specifically lacking either of the key AMPAR subunits, GluA1 or GluA2, in peripheral, pain-sensing neurons (nociceptors), while preserving expression of these subunits in the central nervous system. Nociceptor-specific deletion of GluA1 led to disruption of calcium permeability and reduced capsaicin-evoked activation of nociceptors. Deletion of GluA1, but not GluA2, led to reduced mechanical hypersensitivity and sensitization in models of chronic inflammatory pain and arthritis. Further analysis revealed that GluA1-containing AMPARs regulated the responses of nociceptors to painful stimuli in inflamed tissues and controlled the excitatory drive from the periphery into the spinal cord. Consequently, peripherally applied AMPAR antagonists alleviated inflammatory pain by specifically blocking calcium-permeable AMPARs, without affecting physiological pain or eliciting central side effects. These findings indicate an important pathophysiological role for calcium-permeable AMPARs in nociceptors and may have therapeutic implications for the treatment chronic inflammatory pain states.
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

