A role for antibodies to human leukocyte antigens, collagen-V, and K-α1-Tubulin in antibody-mediated rejection and cardiac allograft vasculopathy
- PMID: 21383658
- PMCID: PMC3722875
- DOI: 10.1097/TP.0b013e318211d2f4
A role for antibodies to human leukocyte antigens, collagen-V, and K-α1-Tubulin in antibody-mediated rejection and cardiac allograft vasculopathy
Abstract
Background: We determined the role of donor-specific antibodies (DSA) and antibodies (Abs) to self-antigens, collagen-V (Col-V), and K-α1-Tubulin (KAT) in pathogenesis of acute antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) and cardiac allograft vasculopathy (CAV) after human heart transplantation (HTx).
Methods: One hundred thirty-seven HTx recipients, with 60 early period (≤ 12 months) and 77 late period (>12 months), were enrolled in this study. Circulating DSA was determined using LUMINEX. Abs against Col-I, II, IV, V, and KAT were measured using ELISA. Frequency of CD4+T helper cells (CD4+Th) secreting interferon (IFN)-γ, interleukin (IL)-5, -10, or -17 specific to self-antigens were determined using Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Spot assay.
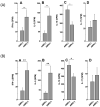
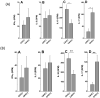
Results: A significant association between AMR and DSA was demonstrated. Development of DSA in AMR patients correlated well with the development of auto-Abs to Col-V (AMR[+]: 383 ± 72 μg/mL, AMR[-]: 172 ± 49 μg/mL, P=0.033) and KAT (AMR[+]: 252 ± 49 μg/mL, AMR[-]: 61 ± 21 μg/mL, P=0.014). Patients who developed AMR demonstrated increased frequencies of CD4+Th secreting IFN-γ and IL-5 with reduction in IL-10 specific for Col-V/KAT. Patients diagnosed with CAV also developed DSA and auto-Abs to Col-V (CAV[+]: 835 ± 142 μg/mL, CAV[-]: 242 ± 68 μg/mL, P=0.025) and KAT (CAV[+]: 768 ± 206 μg/mL, CAV[-]: 196 ± 72 μg/mL, P=0.001) with increased frequencies of CD4+Th secreting IL-17 with reduction in IL-10 specific for Col-V/KAT. CONCLUSIONS.: Development of Abs to human leukocyte antigens and self-antigens are associated with increases in CD4+Th secreting IFN-γ and IL-5 in AMR and IL-17 in CAV, with reduction in CD4+Th secreting IL-10 in both AMR and CAV.
Figures
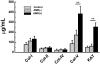


Similar articles
-
Characterization of immune responses to cardiac self-antigens myosin and vimentin in human cardiac allograft recipients with antibody-mediated rejection and cardiac allograft vasculopathy.J Heart Lung Transplant. 2010 Nov;29(11):1277-85. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2010.05.025. Epub 2010 Jul 7. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2010. PMID: 20615726 Free PMC article.
-
Donor-specific antibodies to human leukocyte antigens are associated with and precede antibodies to major histocompatibility complex class I-related chain A in antibody-mediated rejection and cardiac allograft vasculopathy after human cardiac transplantation.Hum Immunol. 2010 Dec;71(12):1191-6. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2010.09.012. Epub 2010 Sep 21. Hum Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20868717 Free PMC article.
-
Alloimmunity-induced autoimmunity as a potential mechanism in the pathogenesis of chronic rejection of human lung allografts.J Heart Lung Transplant. 2011 Jun;30(6):624-31. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2011.01.708. Epub 2011 Mar 16. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2011. PMID: 21414808 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between immune responses to HLA and non-HLA self-antigens in allograft rejection.Hum Immunol. 2013 Nov;74(11):1478-85. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Jul 19. Hum Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23876679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antihuman leukocyte antigen antibody-induced autoimmunity: role in chronic rejection.Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2010 Feb;15(1):16-20. doi: 10.1097/MOT.0b013e3283342780. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2010. PMID: 19898237 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
T regulatory cells play a significant role in modulating MHC class I antibody-induced obliterative airway disease.Am J Transplant. 2012 Oct;12(10):2663-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2012.04191.x. Epub 2012 Jul 23. Am J Transplant. 2012. PMID: 22822907 Free PMC article.
-
Effector B cells in cardiac allograft vasculopathy.Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2019 Feb;24(1):31-36. doi: 10.1097/MOT.0000000000000591. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2019. PMID: 30480642 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Significances of Anti-Collagen Type I and Type III Antibodies in Antibody-Mediated Rejection.Transpl Int. 2022 May 11;35:10099. doi: 10.3389/ti.2022.10099. eCollection 2022. Transpl Int. 2022. PMID: 35634584 Free PMC article.
-
Immune responses to self-antigens (autoimmunity) in allograft rejection.Clin Transpl. 2012:261-72. Clin Transpl. 2012. PMID: 23721031 Free PMC article.
-
Antibodies to MHC class II molecules induce autoimmunity: critical role for macrophages in the immunopathogenesis of obliterative airway disease.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e42370. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042370. Epub 2012 Aug 10. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22900015 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kfoury AG, Hammond ME. Controversies in defining cardiac antibody-mediated rejection: need for updated criteria. J Heart Lung Transplant. 29(4):389–394. - PubMed
-
- Kfoury AG, Hammond ME, Snow GL, Stehlik J, Reid BB, Long JW, Gilbert EM, Bader FM, Bull DA, Renlund DG. Early screening for antibody-mediated rejection in heart transplant recipients. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2007;26(12):1264–1269. - PubMed
-
- Almuti K, Haythe J, Dwyer E, Itescu S, Burke E, Green P, Marboe C, Mancini D. The changing pattern of humoral rejection in cardiac transplant recipients. Transplantation. 2007;84(4):498–503. - PubMed
-
- Reed EF, Demetris AJ, Hammond E, Itescu S, Kobashigawa JA, Reinsmoen NL, Rodriguez ER, Rose M, Stewart S, Suciu-Foca N, Zeevi A, Fishbein MC. Acute antibody-mediated rejection of cardiac transplants. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2006;25(2):153–159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

