DHA improves cognition and prevents dysfunction of entorhinal cortex neurons in 3xTg-AD mice
- PMID: 21383850
- PMCID: PMC3044176
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017397
DHA improves cognition and prevents dysfunction of entorhinal cortex neurons in 3xTg-AD mice
Abstract
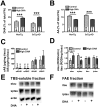
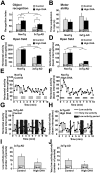
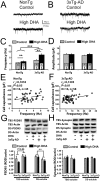
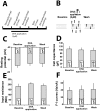
Defects in neuronal activity of the entorhinal cortex (EC) are suspected to underlie the symptoms of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Whereas neuroprotective effects of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) have been described, the effects of DHA on the physiology of EC neurons remain unexplored in animal models of AD. Here, we show that DHA consumption improved object recognition (↑12%), preventing deficits observed in old 3xTg-AD mice (↓12%). Moreover, 3xTg-AD mice displayed seizure-like akinetic episodes, not detected in NonTg littermates and partly prevented by DHA (↓50%). Patch-clamp recording revealed that 3xTg-AD EC neurons displayed (i) loss of cell capacitance (CC), suggesting reduced membrane surface area; (ii) increase of firing rate versus injected current (F-I) curve associated with modified action potentials, and (iii) overactivation of glutamatergic synapses, without changes in synaptophysin levels. DHA consumption increased CC (↑12%) and decreased F-I slopes (↓21%), thereby preventing the opposite alterations observed in 3xTg-AD mice. Our results indicate that cognitive performance and basic physiology of EC neurons depend on DHA intake in a mouse model of AD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Duyckaerts C. Looking for the link between plaques and tangles. Neurobiol Aging. 2004;25:735–739; discussion 743-736. - PubMed
-
- Counts SE, Nadeem M, Lad SP, Wuu J, Mufson EJ. Differential expression of synaptic proteins in the frontal and temporal cortex of elderly subjects with mild cognitive impairment. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2006;65:592–601. - PubMed
-
- Scheff SW, Price DA. Alzheimer's disease-related alterations in synaptic density: neocortex and hippocampus. J Alzheimers Dis. 2006;9:101–115. - PubMed
-
- Palop JJ, Chin J, Mucke L. A network dysfunction perspective on neurodegenerative diseases. Nature. 2006;443:768–773. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

