TRPM2, calcium and neurodegenerative diseases
Abstract
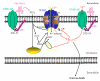
NMDA receptor overactivation triggers intracellular Ca(2+) dysregulation, which has long been thought to be critical for initiating excitotoxic cell death cascades associated with stroke and neurodegenerative disease. The inability of NMDA receptor antagonists to afford neuroprotection in clinical stroke trials has led to a re-evaluation of excitotoxic models of cell death and has focused research efforts towards identifying additional Ca(2+) influx pathways. Recent studies indicate that TRPM2, a member of the TRPM subfamily of Ca(2+)-permeant, non-selective cation channel, plays an important role in mediating cellular responses to a wide range of stimuli that, under certain situations, can induce cell death. These include reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, tumour necrosis factor as well as soluble oli-gomers of amyloid beta. However, the molecular basis of TRPM2 channel involvement in these processes is not fully understood. In this review, we summarize recent studies about the regulation of TRPM2, its interaction with calcium and the possible implications for neurodegenerative diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Aarts M, lihara K, Wei WL, Xiong ZG, Arundine M, Cerwinski W, MacDonald JF, Tymianski M. A key role for TRPM7 channels in anoxic neuronal death. Cell. 2003;115:863–877. 26-12- - PubMed
-
- Xiong ZG, Zhu XM, Chu XP, Minami M, Hey J, Wei WL, MacDonald JF, Wemmie JA, Price MP, Welsh MJ, Simon RP. Neuroprotection in ischemia: blocking calcium-permeable acid-sensing ion channels. Cell. 2004;118:687–698. 17-9- - PubMed
-
- Thompson RJ, Zhou N, MacVicar BA. Ischemia opens neuronal gap junction hemichannels. Science. 2006;312:924–927. 12-5- - PubMed
-
- Lipski J, Park TI, Li D, Lee SC, Trevarton AJ, Chung KK, Freestone PS, Bai JZ. Involvement of TRP-like channels in the acute ischemic response of hippocampal CA1 neurons in brain slices. Brain Res. 2006;1077:187–199. 10-3- - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous