The nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase (NOX) homologues NOX1 and NOX2/gp91(phox) mediate hepatic fibrosis in mice
- PMID: 21384410
- PMCID: PMC3082608
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.24281
The nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase (NOX) homologues NOX1 and NOX2/gp91(phox) mediate hepatic fibrosis in mice
Abstract
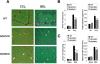
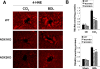
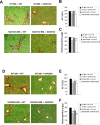
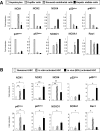
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase (NOX) is a multicomponent enzyme that mediates electron transfer from nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate to molecular oxygen, which leads to the production of superoxide. NOX2/gp91(phox) is a catalytic subunit of NOX expressed in phagocytic cells. Several homologues of NOX2, including NOX1, have been identified in nonphagocytic cells. We investigated the contributory role of NOX1 and NOX2 in hepatic fibrosis. Hepatic fibrosis was induced in wild-type (WT) mice, NOX1 knockout (NOX1KO) mice, and NOX2 knockout (NOX2KO) mice by way of either carbon tetrachloride (CCl(4) ) injection or bile duct ligation (BDL). The functional contribution of NOX1 and NOX2 in endogenous liver cells, including hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), and bone marrow (BM)-derived cells, including Kupffer cells (KCs), to hepatic reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and hepatic fibrosis was assessed in vitro and in vivo using NOX1 or NOX2 BM chimeric mice. Hepatic NOX1 and NOX2 messenger RNA expression was increased in the two experimental mouse models of hepatic fibrosis. Whereas NOX1 was expressed in HSCs but not in KCs, NOX2 was expressed in both HSCs and KCs. Hepatic fibrosis and ROS generation were attenuated in both NOX1KO and NOX2KO mice after CCl(4) or BDL. Liver fibrosis in chimeric mice indicated that NOX1 mediates the profibrogenic effects in endogenous liver cells, whereas NOX2 mediates the profibrogenic effects in both endogenous liver cells and BM-derived cells. Multiple NOX1 and NOX2 components were up-regulated in activated HSCs. Both NOX1- and NOX2-deficient HSCs had decreased ROS generation and failed to up-regulate collagen α1(I) and transforming growth factor β in response to angiotensin II.
Conclusion: Both NOX1 and NOX2 have an important role in hepatic fibrosis in endogenous liver cells, including HSCs, whereas NOX2 has a lesser role in BM-derived cells.
Copyright © 2011 American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase in experimental liver fibrosis: GKT137831 as a novel potential therapeutic agent.Hepatology. 2012 Dec;56(6):2316-27. doi: 10.1002/hep.25938. Hepatology. 2012. PMID: 22806357 Free PMC article.
-
NOX1/nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, reduced form (NADPH) oxidase promotes proliferation of stellate cells and aggravates liver fibrosis induced by bile duct ligation.Hepatology. 2011 Sep 2;54(3):949-58. doi: 10.1002/hep.24465. Epub 2011 Jul 27. Hepatology. 2011. PMID: 21618578
-
Role and cellular source of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase in hepatic fibrosis.Hepatology. 2010 Oct;52(4):1420-30. doi: 10.1002/hep.23804. Hepatology. 2010. PMID: 20690191 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase (NOX) and liver fibrosis: A review.Cell Biochem Funct. 2018 Aug;36(6):292-302. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3351. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Cell Biochem Funct. 2018. PMID: 30028028 Review.
-
Role of NADPH oxidases in liver fibrosis.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014 Jun 10;20(17):2854-72. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5619. Epub 2014 Jan 24. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014. PMID: 24040957 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Strategies and endpoints of antifibrotic drug trials: Summary and recommendations from the AASLD Emerging Trends Conference, Chicago, June 2014.Hepatology. 2015 Aug;62(2):627-34. doi: 10.1002/hep.27720. Epub 2015 Mar 10. Hepatology. 2015. PMID: 25626988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Hepatic Fibrosis in Autoimmune Hepatitis.Dig Dis Sci. 2016 Nov;61(11):3118-3139. doi: 10.1007/s10620-016-4254-7. Epub 2016 Jul 19. Dig Dis Sci. 2016. PMID: 27435327 Review.
-
Docosahexaenoic acid attenuates hepatic inflammation, oxidative stress, and fibrosis without decreasing hepatosteatosis in a Ldlr(-/-) mouse model of western diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.J Nutr. 2013 Mar;143(3):315-23. doi: 10.3945/jn.112.171322. Epub 2013 Jan 9. J Nutr. 2013. PMID: 23303872 Free PMC article.
-
Antifibrotic therapies in the liver.Semin Liver Dis. 2015 May;35(2):184-98. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1550055. Epub 2015 May 14. Semin Liver Dis. 2015. PMID: 25974903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of NADPH Oxidases (NOXs) in Liver Fibrosis and the Activation of Myofibroblasts.Front Physiol. 2016 Feb 2;7:17. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00017. eCollection 2016. Front Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26869935 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bubici C, Papa S, Dean K, Franzoso G. Mutual cross-talk between reactive oxygen species and nuclear factor-kappa B: molecular basis and biological significance. Oncogene. 2006;25:6731–6748. - PubMed
-
- Parola M, Robino G. Oxidative stress-related molecules and liver fibrosis. J Hepatol. 2001;35:297–306. - PubMed
-
- Nieto N, Greenwel P, Friedman SL, Zhang F, Dannenberg AJ, Cederbaum AI. Ethanol and arachidonic acid increase alpha 2(I) collagen expression in rat hepatic stellate cells overexpressing cytochrome P450 2E1. Role of H2O2 and cyclooxygenase-2. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:20136–20145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
