Power-law dependence of the melting temperature of ubiquitin on the volume fraction of macromolecular crowders
- PMID: 21385002
- PMCID: PMC3064690
- DOI: 10.1063/1.3556671
Power-law dependence of the melting temperature of ubiquitin on the volume fraction of macromolecular crowders
Abstract
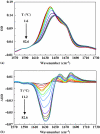
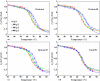
The dependence of the melting temperature increase (ΔT(m)) of the protein ubiquitin on the volume fraction (ϕ) of several commonly used macromolecular crowding agents (dextran 6, 40, and 70 and ficoll 70) was quantitatively examined and compared to a recently developed theoretical crowding model, i.e., ΔT(m) ∼ (R(g)∕R(c))(α)φ(α∕3). We found that in the current case this model correctly predicts the power-law dependence of ΔT(m) on φ but significantly overestimates the role of the size (i.e., R(c)) of the crowding agent. In addition, we found that for ubiquitin the exponent α is in the range of 4.1-6.5, suggesting that the relation of α=3∕(3ν-1) is a better choice for estimating α based on the Flory coefficient (ν) of the polypeptide chain. Taken together these findings highlight the importance of improving our knowledge and theoretical treatment of the microcompartmentalization of the commonly used model crowding agents.
© 2011 American Institute of Physics.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

