Analyses of phylogeny, evolution, conserved sequences and genome-wide expression of the ICK/KRP family of plant CDK inhibitors
- PMID: 21385782
- PMCID: PMC3091803
- DOI: 10.1093/aob/mcr034
Analyses of phylogeny, evolution, conserved sequences and genome-wide expression of the ICK/KRP family of plant CDK inhibitors
Abstract
Background and aims: The cell cycle is controlled by cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), and CDK inhibitors are major regulators of their activities. The ICK/KRP family of CDK inhibitors has been reported in several plants, with seven members in arabidopsis; however, the phylogenetic relationship among members in different species is unknown. Also, there is a need to understand how these genes and proteins are regulated. Furthermore, little information is available on the functional differences among ICK/KRP family members.
Methods: We searched publicly available databases and identified over 120 unique ICK/KRP protein sequences from more than 60 plant species. Phylogenetic analysis was performed using 101 full-length sequences from 40 species and intron-exon organization of ICK/KRP genes in model species. Conserved sequences and motifs were analysed using ICK/KRP protein sequences from arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), rice (Oryza sativa) and poplar (Populus trichocarpa). In addition, gene expression was examined using microarray data from arabidopsis, rice and poplar, and further analysed by RT-PCR for arabidopsis.
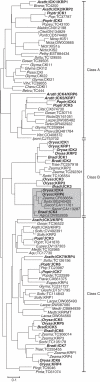
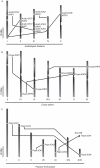
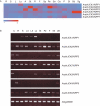
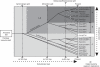
Key results and conclusions: Phylogenetic analysis showed that plant ICK/KRP proteins can be grouped into three major classes. Whereas the C-class contains sequences from dicotyledons, monocotyledons and gymnosperms, the A- and B-classes contain only sequences from dicotyledons or monocotyledons, respectively, suggesting that the A- and B-classes might have evolved from the C-class. This classification is also supported by exon-intron organization. Genes in the A- and B- classes have four exons, whereas genes in the C-class have only three exons. Analysis of sequences from arabidopsis, rice and poplar identified conserved sequence motifs, some of which had not been described previously, and putative functional sites. The presence of conserved motifs in different family members is consistent with the classification. In addition, gene expression analysis showed preferential expression of ICK/KRP genes in certain tissues. A model has been proposed for the evolution of this gene family in plants.
Figures




References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. Journal of Molecular Biology. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Bailey TL, Elkan C. Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers. In: Altman R, Brutlag D, Karp P, Lathrop R, Searls D, editors. Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Intelligent Systems for Molecular Biology. Menlo Park, CA: AAAI Press; 1994. pp. 28–36. - PubMed
-
- Bailey TL, Gribskov M. Combining evidence using p-values: application to sequence homology searches. Bioinformatics. 1998;14:48–54. - PubMed
-
- Bemis SM, Torii KU. Autonomy of cell proliferation and developmental programs during Arabidopsis aboveground organ morphogenesis. Developmental Biology. 2007;304:367–381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

