Effect of basic fibroblast growth factor and cytochrome c peroxidase combination in transgenic mice corneal epithelial healing process after excimer laser photoablation
- PMID: 21386914
- PMCID: PMC3046991
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S16866
Effect of basic fibroblast growth factor and cytochrome c peroxidase combination in transgenic mice corneal epithelial healing process after excimer laser photoablation
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the role of prepared basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) and cytochrome c peroxidase (CCP) combination eyedrops in corneal epithelial healing of transgenic mice (B6(A)-Rpe(rd12)/J) after excimer laser photoablation.
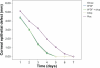
Materials and methods: In this prospective study, 216 eyes of 108 mice underwent bilateral photorefractive keratectomy. We considered 4 groups: A, B, C, and D. Group A received standard topical postoperative therapy with tobramycin, diclofenac, and dexamethasone eyedrops plus CCP at 3 drops per day for a week or until corneal re-epithelialization was achieved. Group B received standard topical postoperative therapy plus bFGF eyedrops and phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) 3 drops per day for a week or until corneal re-epithelialization was complete. In group C, 1 eye received standard topical postoperative therapy plus CCP eyedrops, bFGF eyedrops, and PBS 3 drops per day for a week or until corneal re-epithelialization was complete. Control eyes (group D) received a standard topical postoperative therapy plus placebo eyedrops. Mice were followed-up for a week from the day after the surgery to evaluate the rate of corneal re-epithelialization.
Results: Data were analyzed by ANOVA using the XLSTAT 2010 software. Eyes in group A, B, and C healed completely before the fifth postoperative day, achieving, respectively, a re-epithelialization time of 92 hours ± 10 SD, 90 hours ± 12 SD, and 86 hours ± 12 SD. Group D had a re-epithelialization time of 121 hours ± 8 SD (P < 0.05). No side effects or toxic effects were documented.
Conclusions: Results suggest that re-epithelialization after phototherapeutic keratectomy can benefit from topical therapy with CCP/bFGF combination eyedrops. Further clinical studies are needed to evaluate the long-term effectiveness of these eyedrops to prevent corneal haze.
Keywords: bFGF; corneal wound healing; cytochrome c peroxidase; excimer laser photoablation; refractive surgery; transgenic mice.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of cytochrome c peroxidase on the corneal epithelial healing process after excimer laser photo-ablation in transgenic mice.Eur Surg Res. 2007;39(2):82-7. doi: 10.1159/000099147. Epub 2007 Feb 1. Eur Surg Res. 2007. PMID: 17283431
-
Effect of basic fibroblast growth factor in transgenic mice: corneal epithelial healing process after excimer laser photoablation.Ophthalmologica. 2009;223(2):139-44. doi: 10.1159/000187686. Epub 2008 Dec 18. Ophthalmologica. 2009. PMID: 19092284
-
Effect of cysteine in transgenic mice on healing of corneal epithelium after excimer laser photoablation.Ophthalmologica. 2008;222(6):380-5. doi: 10.1159/000151691. Epub 2008 Aug 28. Ophthalmologica. 2008. PMID: 18753800
-
Effect of cytochrome c peroxidase on corneal epithelial healing process after photorefractive keratectomy.J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005 Oct;31(10):1928-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2005.03.076. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005. PMID: 16338562 Clinical Trial.
-
Meta-analysis: clinical outcomes of laser-assisted subepithelial keratectomy and photorefractive keratectomy in myopia.Ophthalmology. 2010 Oct;117(10):1912-22. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2010.02.004. Epub 2010 Aug 14. Ophthalmology. 2010. PMID: 20709406
Cited by
-
Meibomian Gland Dysfunction: What Have Animal Models Taught Us?Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 21;21(22):8822. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228822. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33233466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of transepithelial and conventional photorefractive keratectomy in myopic and myopic astigmatism patients: a randomized contralateral trial.BMC Ophthalmol. 2022 Feb 11;22(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s12886-022-02293-2. BMC Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35148689 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Oral l-Cysteine Supplementation Enhances the Long Term-Effect of Topical Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor (bFGF) in Reducing the Corneal Haze after Photorefractive Keratectomy in Myopic Patients.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020 Apr 15;13(4):67. doi: 10.3390/ph13040067. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32326563 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotrophic Keratopathy in Systemic Diseases: A Case Series on Patients Treated With rh-NGF.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 May 30;9:920688. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.920688. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35707524 Free PMC article.
-
The Application of Artificial Neural Networks and Logistic Regression in the Evaluation of Risk for Dry Eye after Vitrectomy.J Ophthalmol. 2020 Apr 21;2020:1024926. doi: 10.1155/2020/1024926. eCollection 2020. J Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32377409 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Paysse EA, Hamill MB, Koch DD, et al. Epithelial healing and ocular discomfort after photorefractive keratectomy in children. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003;29:478–481. - PubMed
-
- Kuo IC. Corneal wound healing. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2004;15:311–315. - PubMed
-
- Patel GM, Chuang AZ, Kiang E, et al. Epithelial healing rates with topical ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin and ofloxacin, with artificial tears after photorefractive keratectomy. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000;26:690–694. - PubMed
-
- Hersh PS, Stulting RD, Steinert RF, et al. Results of phase III excimer laser photorefractive keratectomy for myopia. The Summit PRK Study Group. Ophthalmology. 1997;104:1535–1553. - PubMed
-
- Kasetsuwan N, Wu FM, Hsieh F, et al. Effect of topical ascorbic acid on free radical tissue damage and inflammatory cell influx in the cornea after excimer laser corneal surgery. Arch Ophthalmol. 1999;117:649–652. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

