Downregulation of VRK1 by p53 in response to DNA damage is mediated by the autophagic pathway
- PMID: 21386980
- PMCID: PMC3046209
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017320
Downregulation of VRK1 by p53 in response to DNA damage is mediated by the autophagic pathway
Abstract
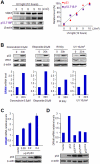
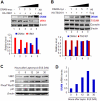
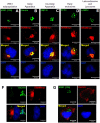
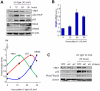
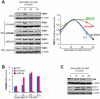
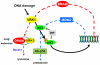
Human VRK1 induces a stabilization and accumulation of p53 by specific phosphorylation in Thr18. This p53 accumulation is reversed by its downregulation mediated by Hdm2, requiring a dephosphorylated p53 and therefore also needs the removal of VRK1 as stabilizer. This process requires export of VRK1 to the cytosol and is inhibited by leptomycin B. We have identified that downregulation of VRK1 protein levels requires DRAM expression, a p53-induced gene. DRAM is located in the endosomal-lysosomal compartment. Induction of DNA damage by UV, IR, etoposide and doxorubicin stabilizes p53 and induces DRAM expression, followed by VRK1 downregulation and a reduction in p53 Thr18 phosphorylation. DRAM expression is induced by wild-type p53, but not by common human p53 mutants, R175H, R248W and R273H. Overexpression of DRAM induces VRK1 downregulation and the opposite effect was observed by its knockdown. LC3 and p62 were also downregulated, like VRK1, in response to UV-induced DNA damage. The implication of the autophagic pathway was confirmed by its requirement for Beclin1. We propose a model with a double regulatory loop in response to DNA damage, the accumulated p53 is removed by induction of Hdm2 and degradation in the proteasome, and the p53-stabilizer VRK1 is eliminated by the induction of DRAM that leads to its lysosomal degradation in the autophagic pathway, and thus permitting p53 degradation by Hdm2. This VRK1 downregulation is necessary to modulate the block in cell cycle progression induced by p53 as part of its DNA damage response.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Sengupta S, Harris CC. p53: traffic cop at the crossroads of DNA repair and recombination. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:44–55. - PubMed
-
- Horn HF, Vousden KH. Coping with stress: multiple ways to activate p53. Oncogene. 2007;26:1306–1316. - PubMed
-
- Baehrecke EH. Autophagy: dual roles in life and death? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:505–510. - PubMed
-
- Saito S, Yamaguchi H, Higashimoto Y, Chao C, Xu Y, et al. Phosphorylation Site Interdependence of Human p53 Post-translational Modifications in Response to Stress. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:37536–37544. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

