Acupuncture for sequelae of Bell's palsy: a randomized controlled trial protocol
- PMID: 21388554
- PMCID: PMC3062611
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-12-71
Acupuncture for sequelae of Bell's palsy: a randomized controlled trial protocol
Abstract
Objective: Incomplete recovery from facial palsy has a long-term impact on the quality of life, and medical options for the sequelae of Bell's palsy are limited. Invasive treatments and physiotherapy have been employed to relieve symptoms, but there is limited clinical evidence for their effectiveness. Acupuncture is widely used on Bell's palsy patients in East Asia, but there is insufficient evidence for its effectiveness on Bell's palsy sequelae. The objective is to evaluate the efficacy and safety of acupuncture in patients with sequelae of Bell's palsy.
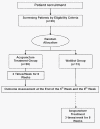
Method/design: This study consists of a randomized controlled trial with two parallel arms: an acupuncture group and a waitlist group. The acupuncture group will receive acupuncture treatment three times per week for a total of 24 sessions over 8 weeks. Participants in the waitlist group will not receive any acupuncture treatments during this 8 week period, but they will participate in the evaluations of symptoms at the start of the study, at 5 weeks and at 8 weeks after randomization, at which point the same treatment as the acupuncture group will be provided. The primary outcome will be analyzed by the change in the Facial Disability Index (FDI) from baseline to week eight. The secondary outcome measures will include FDI from baseline to week five, House-Brackmann Grade, lip mobility, and stiffness scales.
Figures
References
-
- Holland J. Bell's palsy. Clin Evid (Online) 2008;2008
-
- Murakami S, Mizobuchi M, Nakashiro Y, Doi T, Hato N, Yanagihara N. Bell palsy and herpes simplex virus: identification of viral DNA in endoneurial fluid and muscle. Ann Intern Med. 1996;124:27–30. - PubMed
-
- Peitersen E. Bell's palsy: the spontaneous course of 2,500 peripheral facial nerve palsies of different etiologies. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 2002;122:4–30. - PubMed
-
- Devriese PP. Treatment of sequelae after facial paralysis: a global approach. J Laryngol Otol. 1998;112:429–431. - PubMed
-
- Beurskens CH, Heymans PG. Mime therapy improves facial symmetry in people with long-term facial nerve paresis: a randomised controlled trial. Aust J Physiother. 2006;52:177–183. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical