Roles of chromatin remodeling factors in the formation and maintenance of heterochromatin structure
- PMID: 21388962
- PMCID: PMC3077663
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.183269
Roles of chromatin remodeling factors in the formation and maintenance of heterochromatin structure
Abstract
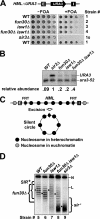
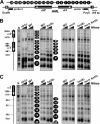
Heterochromatin consists of highly ordered nucleosomes with characteristic histone modifications. There is evidence implicating chromatin remodeling proteins in heterochromatin formation, but their exact roles are not clear. We demonstrate in Saccharomyces cerevisiae that the Fun30p and Isw1p chromatin remodeling factors are similarly required for transcriptional silencing at the HML locus, but they differentially contribute to the structure and stability of HML heterochromatin. In the absence of Fun30p, only a partially silenced structure is established at HML. Such a structure resembles fully silenced heterochromatin in histone modifications but differs markedly from both fully silenced and derepressed chromatin structures regarding nucleosome arrangement. This structure likely represents an intermediate state of heterochromatin that can be converted by Fun30p to the mature state. Moreover, Fun30p removal reduces the rate of de novo establishment of heterochromatin, suggesting that Fun30p assists the silencing machinery in forming heterochromatin. We also find evidence suggesting that Fun30p functions together with, or after, the action of the silencing machinery. On the other hand, Isw1p is dispensable for the formation of heterochromatin structure but is instead critically required for maintaining its stability. Therefore, chromatin remodeling proteins may rearrange nucleosomes during the formation of heterochromatin or serve to stabilize/maintain heterochromatin structure.
Figures







References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

