Netting neutrophils are major inducers of type I IFN production in pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 21389264
- PMCID: PMC3143837
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3001201
Netting neutrophils are major inducers of type I IFN production in pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
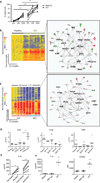
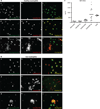
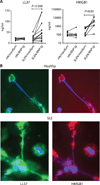
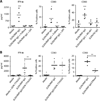
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a systemic autoimmune disease characterized by a breakdown of tolerance to nuclear antigens and the development of immune complexes. Genomic approaches have shown that human SLE leukocytes homogeneously express type I interferon (IFN)-induced and neutrophil-related transcripts. Increased production and/or bioavailability of IFN-α and associated alterations in dendritic cell (DC) homeostasis have been linked to lupus pathogenesis. Although neutrophils have long been shown to be associated with lupus, their potential role in disease pathogenesis remains elusive. Here, we show that mature SLE neutrophils are primed in vivo by type I IFN and die upon exposure to SLE-derived anti-ribonucleoprotein antibodies, releasing neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). SLE NETs contain DNA as well as large amounts of LL37 and HMGB1, neutrophil proteins that facilitate the uptake and recognition of mammalian DNA by plasmacytoid DCs (pDCs). Indeed, SLE NETs activate pDCs to produce high levels of IFN-α in a DNA- and TLR9 (Toll-like receptor 9)-dependent manner. Our results reveal an unsuspected role for neutrophils in SLE pathogenesis and identify a novel link between nucleic acid-recognizing antibodies and type I IFN production in this disease.
Figures

Comment in
-
Dissecting the immune cell mayhem that drives lupus pathogenesis.Sci Transl Med. 2011 Mar 9;3(73):73ps9. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002138. Sci Transl Med. 2011. PMID: 21389262 Free PMC article.
-
TRAPping the cellular mechanisms of lupus.EMBO Mol Med. 2011 Oct;3(10):578-80. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201100167. Epub 2011 Sep 9. EMBO Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21905225 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lahita RG. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. ed. 3. San Diego: Academic Press; 1999.
-
- Wakeland EK, Liu K, Graham RR, Behrens TW. Delineating the genetic basis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunity. 2001;15:397–408. - PubMed
-
- Rozzo SJ, Allard JD, Choubey D, Vyse TJ, Izui S, Peltz G, Kotzin BL. Evidence for an interferon-inducible gene, Ifi202, in the susceptibility to systemic lupus. Immunity. 2001;15:435–443. - PubMed
-
- Pascual V, Banchereau J, Palucka AK. The central role of dendritic cells and interferon-α in SLE. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2003;15:548–556. - PubMed
-
- Blanco P, Palucka AK, Gill M, Pascual V, Banchereau J. Induction of dendritic cell differentiation by IFN-α in systemic lupus erythematosus. Science. 2001;294:1540–1543. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

