Antidiabetic and antisteatotic effects of the selective fatty acid synthase (FAS) inhibitor platensimycin in mouse models of diabetes
- PMID: 21389266
- PMCID: PMC3069196
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1002588108
Antidiabetic and antisteatotic effects of the selective fatty acid synthase (FAS) inhibitor platensimycin in mouse models of diabetes
Abstract
Platensimycin (PTM) is a recently discovered broad-spectrum antibiotic produced by Streptomyces platensis. It acts by selectively inhibiting the elongation-condensing enzyme FabF of the fatty acid biosynthesis pathway in bacteria. We report here that PTM is also a potent and highly selective inhibitor of mammalian fatty acid synthase. In contrast to two agents, C75 and cerulenin, that are widely used as inhibitors of mammalian fatty acid synthase, platensimycin specifically inhibits fatty acid synthesis but not sterol synthesis in rat primary hepatocytes. PTM preferentially concentrates in liver when administered orally to mice and potently inhibits hepatic de novo lipogenesis, reduces fatty acid oxidation, and increases glucose oxidation. Chronic administration of platensimycin led to a net reduction in liver triglyceride levels and improved insulin sensitivity in db/+ mice fed a high-fructose diet. PTM also reduced ambient glucose levels in db/db mice. These results provide pharmacological proof of concept of inhibiting fatty acid synthase for the treatment of diabetes and related metabolic disorders in animal models.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: All authors are or were employed by Merck & Company, Inc.
Figures

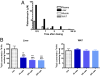
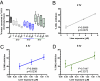

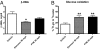
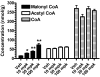
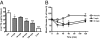
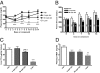
References
-
- Nathan DM, et al. American Diabetes Association European Association for the Study of Diabetes Medical management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: A consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy: A consensus statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009;32:193–203. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cheung BMY, et al. Diabetes prevalence and therapeutic target achievement in the United States, 1999 to 2006. Am J Med. 2009;122:443–453. - PubMed
-
- Singh SB, Phillips JW, Wang J. Highly sensitive target-based whole-cell antibacterial discovery strategy by antisense RNA silencing. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2007;10:160–166. - PubMed
-
- Singh SB, et al. Isolation, structure, and absolute stereochemistry of platensimycin, a broad spectrum antibiotic discovered using an antisense differential sensitivity strategy. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:11916–11920. - PubMed
-
- Wang J, et al. Platensimycin is a selective FabF inhibitor with potent antibiotic properties. Nature. 2006;441:358–361. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

