Understanding dopamine and reinforcement learning: the dopamine reward prediction error hypothesis
- PMID: 21389268
- PMCID: PMC3176615
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1014269108
Understanding dopamine and reinforcement learning: the dopamine reward prediction error hypothesis
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Oct 18;108(42):17568-9
Abstract
A number of recent advances have been achieved in the study of midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Understanding these advances and how they relate to one another requires a deep understanding of the computational models that serve as an explanatory framework and guide ongoing experimental inquiry. This intertwining of theory and experiment now suggests very clearly that the phasic activity of the midbrain dopamine neurons provides a global mechanism for synaptic modification. These synaptic modifications, in turn, provide the mechanistic underpinning for a specific class of reinforcement learning mechanisms that now seem to underlie much of human and animal behavior. This review describes both the critical empirical findings that are at the root of this conclusion and the fantastic theoretical advances from which this conclusion is drawn.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
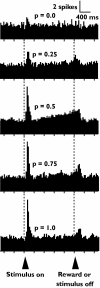
References
-
- Niv Y, Montague PR. Theoretical and empirical studies of learning. In: Glimcher PW, et al., editors. Neuroeconomics: Decision Making and the Brain. New York: Academic Press; 2008. pp. 329–249.
-
- Dayan P, Abbot LF. Theoretical Neuroscience: Computational and Mathematical Modeling of Neural Systems. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press; 2001.
-
- Carlsson A. A Half-Century of Neurotransmitter Research: Impact on Neurology and Psychiatry. Nobel Prize Lecture Presented at Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm. 2000. Available at http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/medicine/laureates/2000/carlsson-lect.... Accessed November 2008.
-
- Fuxe K, et al. The discovery of central monoamine neurons gave volume transmission to the wired brain. Prog Neurobiol. 2010;90:82–100. - PubMed
-
- Cajal SR. Histologie du système nerveux de l'homme & des vertébrés … Édition français revue & mise à jour par l'auteur. 1909-1911 Translated by L. Azoulay. Paris, E. Arrault et Cie for A. Maloine.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

