Serum uric acid level and endothelial dysfunction in patients with nondiabetic chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 21389694
- PMCID: PMC3064939
- DOI: 10.1159/000324847
Serum uric acid level and endothelial dysfunction in patients with nondiabetic chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Background: An elevated serum uric acid level is strongly associated with endothelial dysfunction and inflammation, both of which are common in chronic kidney disease (CKD). We hypothesized that endothelial dysfunction in subjects with CKD would correlate with uric acid levels.
Materials and methods: We evaluated the association between serum uric acid level and ultrasonographic flow-mediated dilatation (FMD) in 263 of 486 patients with recently diagnosed CKD (stage 3-5) (48% male, age 52 ± 12 years). To minimize confounding, 233 patients were excluded because they were diabetic, had established cardiovascular complications or were taking drugs (renin-angiotensin system blockers, statins) interfering with vascular function.
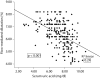
Results: Serum uric acid level was significantly increased in all stages of CKD and strongly correlated with estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR-MDRD); FMD was inversely associated with serum uric acid (r = -0.49, p < 0.001). The association of serum uric acid with FMD remained after adjustment for age, gender, smoking, LDL cholesterol, eGFR, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, systolic blood pressure, proteinuria, and homeostatic model assessment index (β = -0.27, p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Increased serum uric acid is an independent predictor of endothelial dysfunction in subjects with CKD.
Copyright © 2011 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
References
-
- Baylis C. Nitric oxide deficiency in chronic kidney disease. Am J Physiol. 2008;294:F1–F9. - PubMed
-
- Gschwend S, Buikema H, Navis G, Henning RH, de Zeeuw D, van Dokkum RP. Endothelial dilatory function predicts individual susceptibility to renal damage in the 5/6 nephrectomized rat. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13:2909–2915. - PubMed
-
- Ochodnicky P, Vettoretti S, Henning RH, Buikema H, Van Dokkum RP, de Zeeuw D. Endothelial dysfunction in chronic kidney disease: determinant of susceptibility to end-organ damage and therapeutic response. J Nephrol. 2006;19:246–258. - PubMed
-
- Nakagawa T, Sato W, Glushakova O, Heinig M, Clarke T, Campbell-Thompson M, Yuzawa Y, Atkinson MA, Johnson RJ, Croker B. Diabetic endothelial nitric oxide synthase knockout mice develop advanced diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18:539–550. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous