Anti-obesity effects of Lysimachia foenum-graecum characterized by decreased adipogenesis and regulated lipid metabolism
- PMID: 21389766
- PMCID: PMC3085739
- DOI: 10.3858/emm.2011.43.4.025
Anti-obesity effects of Lysimachia foenum-graecum characterized by decreased adipogenesis and regulated lipid metabolism
Abstract
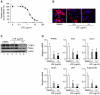
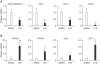
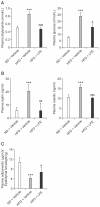
Lysimachia foenum-graecum has been used as an oriental medicine with anti-inflammatory effect. The anti-obesity effect of L. foenum-graecum extract (LFE) was first discovered in our screening of natural product extract library against adipogenesis. To characterize its anti-obesity effects and to evaluate its potential as an anti-obesity drug, we performed various obesity-related experiments in vitro and in vivo. In adipogenesis assay, LFE blocked the differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocyte in a dose-dependent manner with an IC50 of 2.5 μg/ml. In addition, LFE suppressed the expression of lipogenic genes, while increasing the expression of lipolytic genes in vitro at 10 μg/ml and in vivo at 100 mg/kg/day. The anti-adipogenic and anti-lipogenic effect of LFE seems to be mediated by the inhibition of PPARγ and C/EBPα expression as shown in in vitro and in vivo, and the suppression of PPARγ activity in vitro. Moreover, LFE stimulated fatty acid oxidation in an AMPK-dependent manner. In high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obese mice (n = 8/group), oral administration of LFE at 30, 100, and 300 mg/kg/day decreased total body weight gain significantly in all doses tested. No difference in food intake was observed between vehicle- and LFE-treated HFD mice. The weight of white adipose tissues including abdominal subcutaneous, epididymal, and perirenal adipose tissue was reduced markedly in LFE-treated HFD mice in a dose-dependent manner. Treatment of LFE also greatly improved serum levels of obesity-related biomarkers such as glucose, triglycerides, and adipocytokines leptin, adiponectin, and resistin. All together, these results showed anti-obesity effects of LFE on adipogenesis and lipid metabolism in vitro and in vivo and raised a possibility of developing LFE as anti-obesity therapeutics.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Foenumoside B from Lysimachia foenum-graecum inhibits adipocyte differentiation and obesity induced by high-fat diet.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012 Jan 13;417(2):800-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.12.039. Epub 2011 Dec 16. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012. PMID: 22197824
-
Fermented Platycodon grandiflorum Extract Inhibits Lipid Accumulation in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes and High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice.J Med Food. 2016 Nov;19(11):1004-1014. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2016.3805. Epub 2016 Oct 28. J Med Food. 2016. PMID: 27792464
-
Standardized Cirsium setidens Nakai Ethanolic Extract Suppresses Adipogenesis and Regulates Lipid Metabolisms in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes and C57BL/6J Mice Fed High-Fat Diets.J Med Food. 2017 Aug;20(8):763-776. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2017.3965. Epub 2017 Jul 7. J Med Food. 2017. PMID: 28686516
-
Molecular mechanism of down-regulating adipogenic transcription factors in 3T3-L1 adipocyte cells by bioactive anti-adipogenic compounds.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Jan;48(1):743-761. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-06036-8. Epub 2020 Dec 4. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33275195 Review.
-
Anti-obesity effects of medicinal plants from Asian countries and related molecular mechanisms: a review.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Dec 22;22(4):1279-1293. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2204135. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34957770 Review.
Cited by
-
Euterpe oleracea Mart.-Derived Polyphenols Protect Mice from Diet-Induced Obesity and Fatty Liver by Regulating Hepatic Lipogenesis and Cholesterol Excretion.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 2;10(12):e0143721. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143721. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26630290 Free PMC article.
-
Screening of Korean Natural Products for Anti-Adipogenesis Properties and Isolation of Kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside as a Potent Anti-Adipogenetic Compound from Solidago virgaurea.Molecules. 2016 Feb 17;21(2):226. doi: 10.3390/molecules21020226. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 26901177 Free PMC article.
-
HOX-7 suppresses body weight gain and adipogenesis-related gene expression in high-fat-diet-induced obese mice.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Dec 17;14:505. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-505. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 25515293 Free PMC article.
-
1α, 25-dihydroxy Vitamin D3 containing fractions of Catharanthus roseus leaf aqueous extract inhibit preadipocyte differentiation and induce lipolysis in 3T3-L1 cells.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019 Nov 29;19(1):338. doi: 10.1186/s12906-019-2754-7. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019. PMID: 31783835 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of lipid accumulation by the ethyl acetate fraction of Distylium racemosum in vitro and in vivo.Toxicol Rep. 2019 Feb 23;6:215-221. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2019.02.003. eCollection 2019. Toxicol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30891421 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray GA, Tartaglia LA. Medicinal strategies in the treatment of obesity. Nature. 2000;404:672–677. - PubMed
-
- Brun RP, Kim JB, Hu E, Altiok S, Spiegelman BM. Adipocyte differentiation: a transcriptional regulatory cascade. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996;8:826–832. - PubMed
-
- Diez JJ, Iglesias P. The role of the novel adipocyte-derived hormone adiponectin in human disease. Eur J Endocrinol. 2003;148:293–300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
