The results of cervical nucleoplasty in patients with cervical disc disorder: a retrospective clinical study of 22 patients
- PMID: 21390177
- PMCID: PMC3049975
- DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2011.24.1.36
The results of cervical nucleoplasty in patients with cervical disc disorder: a retrospective clinical study of 22 patients
Abstract
Background: Nucleoplasty is a minimally invasive spinal surgery using a Coblation® technique that creates small voids within the disc. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of cervical nucleoplasty in patients with cervical disc disorder.
Methods: Between March 2008 and December 2009, 22 patients with cervical disc disorders were treated with cervical nucleoplasty after failed conservative treatment. All procedures were performed under local anesthesia, and fluoroscopic guidance and voids were created in the disc with the Perc™ DC Spine Wand™. Clinical outcomes were evaluated by the Modified Macnab criteria and VAS score at preprocedure, postprocedure 1 month, and 6 months.
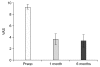
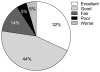
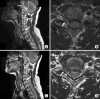
Results: Six patients had one, eight patients had two and eight patients had three discs treated; a total of 46 procedures was performed. Mean VAS reduced from 9.3 at preprocedure to 3.7 at postprocedure 1 month and to 3.4 at postprocedure 6 months. There was no significant complication related to the procedure within the first month. Outcomes were good or excellent in 17/22 (77.3%) cases. Postprocedure magnetic resonance imaging was acquired in two patients after two months showing morphologic evidence of volume reduction of protruded disc material in one patient but not in the other.
Conclusions: Percutaneous decompression with a nucleoplasty using a Coblation® technique in the treatment of cervical disc disorder is a safe, minimally-invasive and less uncomfortable procedure, with an excellent short-term clinical outcome.
Keywords: cervical; disc; diskectomy; nucleoplasty; percutaneous.
Figures


References
-
- Nardi PV, Cabezas D, Cesaroni A. Percutaneous cervical nucleoplasty using coblation technology. Clinical results in fifty consecutive cases. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2005;92:73–78. - PubMed
-
- Sharps LS, Isaac Z. Percutaneous disc decompression using nucleoplasty. Pain Physician. 2002;5:121–126. - PubMed
-
- Singh V, Piryani C, Liao K, Nieschulz S. Percutaneous disc decompression using coblation (nucleoplasty) in the treatment of chronic discogenic pain. Pain Physician. 2002;5:250–259. - PubMed
-
- Ro JY, Oh CS, Kim OS, Kim DK, Woo NS, Shin HY. Nucleoplasty in a patient with cervical disc extrusion with radiating pain of an upper extremity. Anesth Pain Med. 2009;4:203–207.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
