A candidate approach implicates the secreted Salmonella effector protein SpvB in P-body disassembly
- PMID: 21390246
- PMCID: PMC3046968
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017296
A candidate approach implicates the secreted Salmonella effector protein SpvB in P-body disassembly
Abstract
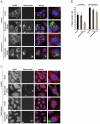
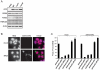
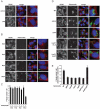
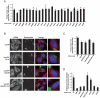
P-bodies are dynamic aggregates of RNA and proteins involved in several post-transcriptional regulation processes. P-bodies have been shown to play important roles in regulating viral infection, whereas their interplay with bacterial pathogens, specifically intracellular bacteria that extensively manipulate host cell pathways, remains unknown. Here, we report that Salmonella infection induces P-body disassembly in a cell type-specific manner, and independently of previously characterized pathways such as inhibition of host cell RNA synthesis or microRNA-mediated gene silencing. We show that the Salmonella-induced P-body disassembly depends on the activation of the SPI-2 encoded type 3 secretion system, and that the secreted effector protein SpvB plays a major role in this process. P-body disruption is also induced by the related pathogen, Shigella flexneri, arguing that this might be a new mechanism by which intracellular bacterial pathogens subvert host cell function.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Salmonella effector SpvB interferes with intracellular iron homeostasis via regulation of transcription factor NRF2.FASEB J. 2019 Dec;33(12):13450-13464. doi: 10.1096/fj.201900883RR. Epub 2019 Sep 30. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 31569998
-
Identification of Salmonella SPI-2 secretion system components required for SpvB-mediated cytotoxicity in macrophages and virulence in mice.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2008 Mar;52(2):194-201. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2007.00364.x. Epub 2008 Jan 31. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18248436
-
Salmonella Effector SpvB Disrupts Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Integrity for Bacterial Translocation.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Dec 17;10:606541. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.606541. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33392110 Free PMC article.
-
The role of host cell death in Salmonella infections.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005;289:131-50. doi: 10.1007/3-540-27320-4_6. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15791954 Review.
-
New insights into the mode of action of the actin ADP-ribosylating virulence factors Salmonella enterica SpvB and Clostridium botulinum C2 toxin.Eur J Cell Biol. 2011 Nov;90(11):944-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2010.11.007. Epub 2011 Jan 17. Eur J Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21247657 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional screenings reveal different requirements for host microRNAs in Salmonella and Shigella infection.Nat Microbiol. 2020 Jan;5(1):192-205. doi: 10.1038/s41564-019-0614-3. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Nat Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31792428
-
RNA-Seq Transcriptomic Responses of Full-Thickness Dermal Excision Wounds to Pseudomonas aeruginosa Acute and Biofilm Infection.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 28;11(10):e0165312. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165312. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27792773 Free PMC article.
-
Micro-balancing innate immunity to Salmonella.EMBO J. 2011 May 18;30(10):1877-9. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.134. EMBO J. 2011. PMID: 21593727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of host microRNA function uncovers a role for miR-29b-2-5p in Shigella capture by filopodia.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Apr 10;13(4):e1006327. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006327. eCollection 2017 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28394930 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular Bacterial Pathogens Trigger the Formation of U Small Nuclear RNA Bodies (U Bodies) through Metabolic Stress Induction.J Biol Chem. 2015 Aug 21;290(34):20904-20918. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.659466. Epub 2015 Jul 1. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26134566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eulalio A, Behm-Ansmant I, Izaurralde E. P bodies: at the crossroads of post-transcriptional pathways. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:9–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

