The assessment of airway maneuvers and interventions in university Canadian football, ice hockey, and soccer players
- PMID: 21391796
- PMCID: PMC3070498
- DOI: 10.4085/1062-6050-46.2.117
The assessment of airway maneuvers and interventions in university Canadian football, ice hockey, and soccer players
Abstract
Context: Managing an airway in an unconscious athlete is a lifesaving skill that may be made more difficult by the recent changes in protective equipment. Different airway maneuvers and techniques may be required to help ventilate an unconscious athlete who is wearing full protective equipment.
Objective: To assess the effectiveness of different airway maneuvers with football, ice hockey, and soccer players wearing full protective equipment.
Design: Crossover study.
Setting: University sports medicine clinic.
Patients or other participants: A total of 146 university varsity athletes, consisting of 62 football, 45 ice hockey, and 39 soccer players.
Intervention(s): Athletes were assessed for different airway and physical characteristics. Three investigators then evaluated the effectiveness of different bag-valve-mask (BVM) ventilation techniques in supine athletes who were wearing protective equipment while inline cervical spine immobilization was maintained.
Main outcome measure(s): The effectiveness of 1-person BVM ventilation (1-BVM), 2-person BVM ventilation (2-BVM), and inline immobilization and ventilation (IIV) was judged by each investigator for each athlete using a 4-point rating scale.
Results: All forms of ventilation were least difficult in soccer players and most difficult in football players. When compared with 1-BVM, both 2-BVM and IIV were deemed more effective by all investigators for all athletes. Interference from the helmet and stabilizer were common reasons for difficult ventilation in football and ice hockey players.
Conclusions: Sports medicine professionals should practice and be comfortable with different ventilation techniques for athletes wearing full equipment. The use of a new ventilation technique, termed inline immobilization and ventilation, may be beneficial, especially when the number of responders is limited.
Figures



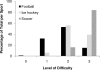

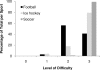

References
-
- Waninger K. N. Management of the helmeted athlete with suspected cervical spine injury. Am J Sports Med. 2004;32(5):1331–1350. - PubMed
-
- Laprade R. F., Schnetzler K. A., Broxterman R. J., Wentorf F., Gilbert T. J. Cervical spine alignment in the immobilized ice hockey player: a computed tomographic analysis of the effects of helmet removal. Am J Sports Med. 2000;28(6):800–803. - PubMed
-
- Gastel J. A., Palumbo M. A., Hulstyn M. J., Fadale P. D., Lucas P. Emergency removal of football equipment: a cadaveric cervical spine injury model. Ann Emerg Med. 1998;32(4):411–417. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

